For people with diabetes, a healthy diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels and preventing complications. This article delves into the fundamentals of diabetic meal planning, explores the different types of carbohydrates and their impact on blood sugar, and provides guidance on making healthy food choices for optimal diabetic health.
Understanding Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar
Carbohydrates (carbs) are the body’s primary source of energy. They break down into glucose (sugar) in the bloodstream, which fuels your cells. However, different types of carbs affect blood sugar levels at varying rates.
- Simple Carbs: These carbs digest quickly, causing a rapid rise in blood sugar. Examples include sugary drinks, white bread, pastries, and processed snacks.
- Complex Carbs: These carbs are digested slower, leading to a more gradual and sustained rise in blood sugar. Examples include whole grains, vegetables, fruits (in moderation), and legumes.
The Glycemic Index (GI)
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a ranking system that assigns a value to foods based on their impact on blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI (above 70) elevate blood sugar rapidly, while those with a low GI (below 50) have a minimal effect.
Fiber: Your Blood Sugar Ally
Fiber, a component of plant-based foods, plays a key role in diabetes management. It slows down digestion, preventing blood sugar spikes, and promotes feelings of fullness, helping with weight control. Sources of fiber include whole grains, fruits (with skin), vegetables, and legumes.
Building a Balanced Diabetic Plate
A balanced diabetic plate incorporates a variety of foods from all food groups while keeping portion sizes in mind. Here’s a breakdown of what to include:
- Non-Starchy Vegetables (Unlimited): Fill half your plate with low-carb, non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, leafy greens, carrots, bell peppers, and mushrooms. These are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Starchy Vegetables (Moderation): Include moderate portions of starchy vegetables like corn, peas, potatoes, and sweet potatoes. Opt for baked or roasted options over fried.
- Lean Protein (Every Meal): Include a source of lean protein at each meal to promote satiety and manage blood sugar levels. Choose skinless chicken, fish, turkey, beans, lentils, low-fat tofu, or eggs.
- Healthy Fats (In Moderation): Include healthy fats like those found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds in moderation. These promote satiety and provide essential nutrients.
- Fruits (In Moderation): While fruits offer vitamins and fiber, they also contain natural sugars. Choose low-glycemic fruits like berries, apples, pears, and grapefruit in moderation.
Making Smart Food Swaps
Simple changes can make a big difference in your diabetic diet. Here are some swaps to consider:
- Swap white bread for whole-wheat bread.
- Swap sugary drinks for water, unsweetened tea, or black coffee.
- Swap white rice for brown rice or quinoa.
- Swap fried foods for baked, grilled, or steamed options.
- Swap sugary snacks for nuts, seeds, or yogurt with berries.
- Swap high-fat meats for lean protein sources.
Reading Food Labels like a Pro
Decoding food labels is crucial for informed choices. Here’s what to pay attention to:
- Serving Size: Be mindful of serving sizes to avoid overconsumption.
- Total Carbohydrates: Focus on the total carbs, not just net carbs (total carbs minus fiber).
- Fiber Content: Aim for foods higher in fiber content.
- Sugar Content: Limit foods with high added sugars.
Planning and Preparing Healthy Meals
Planning and preparation are key for maintaining a healthy diabetic diet. Here are some tips:
- Plan your meals and snacks for the week.
- Create a grocery list based on your meal plan.
- Cook large batches on weekends for easy access throughout the week.
- Prepare healthy snacks in advance to avoid unhealthy choices on the go.
- Pack your lunch to avoid unhealthy restaurant options.
Dining Out with Diabetes
Eating out doesn’t have to derail your healthy eating goals. Here are some tips for navigating restaurants:
- Review menus online beforehand.
- Choose grilled, baked, or steamed options.
- Be mindful of portion sizes.
- Ask for sauces and dressings on the side.
- Limit sugary drinks and opt for water or unsweetened tea.
Managing Special Occasions and Holidays
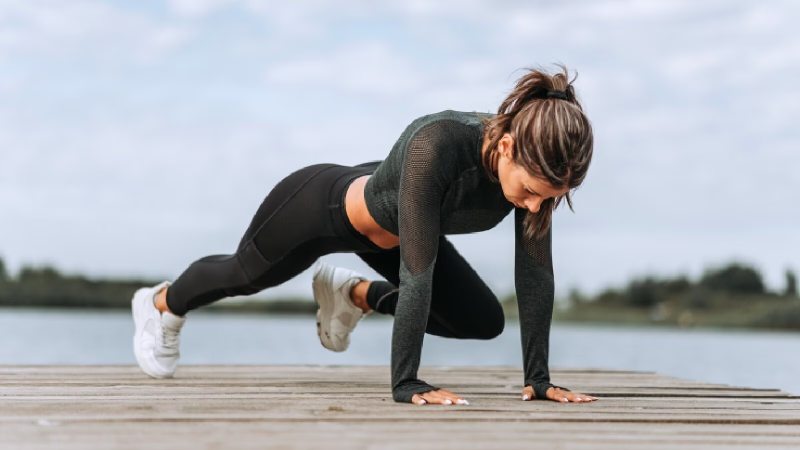
Celebrating holidays and special occasions doesn’t mean abandoning your diabetic diet. Here are For people with diabetes, regular physical activity is not just beneficial, it’s vital. Exercise helps manage blood sugar levels, improve overall health, and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. This article explores the different types of exercise suitable for diabetes management, provides tips for getting started and staying motivated, and addresses common concerns about exercising with diabetes.
The Benefits of Exercise for Diabetes
Exercise offers a multitude of benefits for those living with diabetes, including:
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Physical activity helps your body utilize glucose (sugar) from your bloodstream more effectively, leading to lower blood sugar levels.
- Increased Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise improves your body’s sensitivity to insulin, the hormone that allows cells to absorb glucose.
- Weight Management: Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, which plays a crucial role in diabetes management.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Exercise lowers the risk of developing diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, stroke, and nerve damage.
- Improved Mood and Energy Levels: Physical activity can boost endorphins, hormones that elevate mood and promote feelings of well-being.
- Increased Strength and Flexibility: Exercise can improve muscle strength, flexibility, and balance, making daily activities easier.
Choosing the Right Exercise for You
The best exercise program for diabetes management is one you enjoy and can stick with consistently. Here are different types of exercise to consider:
- Aerobic Exercise: Also known as cardio, this type of exercise gets your heart rate up and increases your breathing. Examples include brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, and dancing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week.
- Strength Training: Building muscle mass through exercises like weightlifting, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises can improve insulin sensitivity and overall strength. Aim for strength training exercises involving major muscle groups at least twice a week.
- Low-Impact Activities: Low-impact exercises like yoga, Pilates, and water aerobics are gentle on your joints and offer flexibility and balance benefits.
Getting Started and Staying Motivated
Starting an exercise routine can be daunting, but here are some tips to overcome the initial hurdle and stay motivated:
- Begin Slowly: Start with a manageable exercise duration and intensity, gradually increasing as your fitness improves.
- Find Activities You Enjoy: Choose activities you find fun and engaging to make exercise feel less like a chore.
- Schedule Your Workouts: Block time in your calendar for exercise and treat it like any other important appointment.
- Find a Workout Buddy: Having a partner can provide encouragement and accountability.
- Track Your Progress: Monitor your progress in a journal or app. Seeing improvements can be a powerful motivator.
- Reward Yourself: Celebrate milestones and achievements to stay motivated.
Safety Considerations for Exercise with Diabetes
While exercise is essential, some precautions are necessary for people with diabetes:
- Consult Your Doctor: Before starting a new exercise program, consult your doctor to ensure it’s safe for you. They may advise specific adjustments based on your health condition.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Check your blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise, particularly if you’re taking insulin or medications that affect blood sugar.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes appropriate for the chosen activity to prevent injuries.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body’s signals. Rest when needed and avoid pushing yourself too hard.
- Carry Emergency Supplies: Always carry identification with your medical information and a quick-acting source of sugar, such as glucose tablets or juice, in case of a hypoglycemic event (low blood sugar).
Conclusion
By incorporating regular physical activity into your life, you can significantly improve your diabetes management and overall well-being. Remember,
By incorporating regular physical activity into your life, you can significantly improve your diabetes management and overall well-being. Remember, even small changes can make a big difference. Start slowly, find activities you enjoy, listen to your body, and don’t be afraid to seek support from your doctor or a certified fitness professional. With dedication and consistency, exercise can become a powerful tool in managing your diabetes and living a healthy and fulfilling life.
Additional Tips:
- Incorporate Activity into Daily Life: Take the stairs instead of the elevator, park further away from your destination, or do jumping jacks during commercial breaks while watching TV. Every bit counts!
- Join a Fitness Class: There are many diabetic-specific or low-impact exercise classes offered at gyms, community centers, or online.
- Explore Outdoor Activities: Hiking, biking, or gardening can be enjoyable ways to get your daily dose of exercise while enjoying nature.
- Find Activities You Can Do with Family and Friends: Exercising with loved ones can make it more fun and create lasting memories.
- Consider Wearable Fitness Trackers: These devices can help you track your activity levels, set goals, and stay motivated.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago








