Have you or someone you know been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes? This unfamiliar territory can be overwhelming. But fear not! This comprehensive guide serves as your roadmap to understanding type 1 diabetes, its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or seeking to expand your knowledge, this guide empowers you to navigate this journey with confidence.
Demystifying Diabetes: Understanding Blood Sugar Control
Before delving into type 1 diabetes, let’s establish a foundation. Our bodies rely on glucose (sugar) from food for energy. The pancreas, a gland located behind the stomach, produces insulin, a hormone that acts like a key, unlocking the doors of your cells and allowing glucose to enter for fuel.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This results in a deficiency or complete absence of insulin production. Without enough insulin, glucose cannot enter the cells effectively, leading to a buildup of sugar in the bloodstream (hyperglycemia).
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes?
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute:
- Genetics: A family history of type 1 diabetes increases the risk.
- Environmental triggers: Certain viruses or exposure to specific environmental factors might play a role, although this is still being researched.
It’s important to understand that type 1 diabetes is not caused by lifestyle factors like diet or exercise.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can develop rapidly, sometimes within a few weeks, and often require immediate medical attention. Here are some key signs to watch out for:
- Increased thirst and urination: The body tries to expel excess sugar through urine, leading to frequent urination and increased thirst.
- Excessive hunger: Cells are starved for energy due to the inability to utilize blood sugar effectively, leading to increased hunger.
- Unexplained weight loss: The body might break down muscle tissue for energy when glucose utilization is impaired.
- Fatigue and tiredness: Cells deprived of glucose experience a lack of energy, leading to fatigue.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the lenses in the eyes, causing blurred vision.
- Slow-healing wounds: High blood sugar levels can impair circulation and healing processes.
- Frequent infections: High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and improve overall health.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes: Management Strategies
While there’s no cure for type 1 diabetes, effective management strategies can help you live a full and healthy life. Here are the cornerstones of successful management:
- Insulin Therapy: Since your body doesn’t produce enough insulin, you’ll need to replace it with external injections. Your doctor will determine the type of insulin, dosage, and injection schedule best suited for your individual needs. There are various types of insulin available, each with different durations of action.
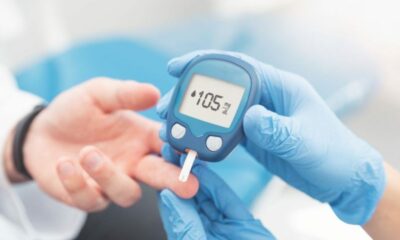
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels using finger pricks and a glucometer or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) is essential. This allows you to adjust insulin intake, diet, and activity based on real-time data.
- Healthy Eating: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is crucial. Focus on portion control and consider consulting a registered dietitian for personalized meal plans.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels. Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to manage stress effectively.
Additional Considerations for Beginners
- Carbohydrate Counting: Understanding how carbohydrates in food affect blood sugar levels is crucial for managing insulin doses.
- Sick Day Management: Illnesses can significantly impact blood sugar control. Develop a plan with your doctor for managing blood sugar during sickness.
- Support System: Connect with a diabetes educator, support groups, or online communities for guidance, motivation, and emotional support.
- Managing Travel and Social Events: With careful planning and adjustments to insulin and meals, you can still enjoy travel and social gatherings.
Living a Fulfilling Life with Type 1 Diabetes
A diagnosis of type 1 diabetes might seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to define your life. By embracing these management strategies and adopting a healthy lifestyle , you can effectively manage your blood sugar and achieve a fulfilling life. Here are some additional tips:
- Develop a positive mindset: Focus on progress, not perfection. Celebrate your achievements and milestones along the way.
- Prioritize sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and blood sugar control. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease. Brush and floss regularly and schedule regular dental checkups.
- Regular doctor visits: Schedule regular appointments with your doctor to monitor your progress, adjust your treatment plan as needed, and address any concerns.
- Stay informed: Stay updated on the latest advancements in diabetes research and technology, such as new insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and potential future treatments.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Millions of people worldwide are living successfully with type 1 diabetes. With knowledge, dedication, and the support of your healthcare team, you can thrive despite this condition.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge and should not be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor to create a personalized diabetes management plan tailored to your specific needs.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago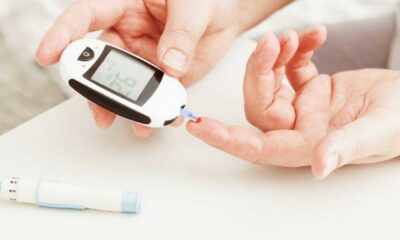
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago