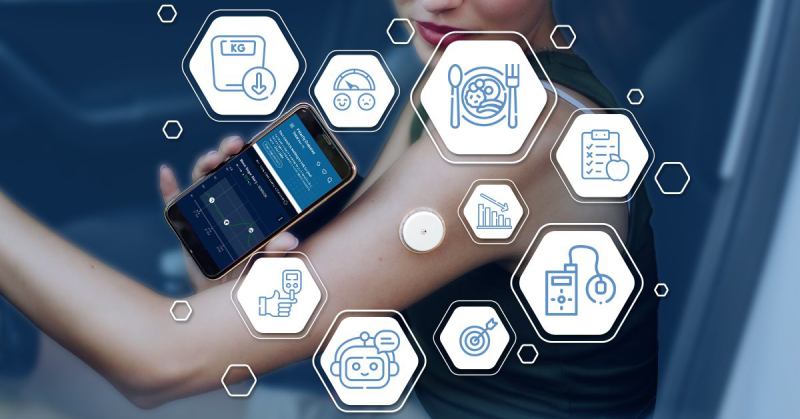
Diabetology
What is the Role of Technology in Diabetes Management?
-

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks agoHow to Identify Prediabetes: Key Risk Factors and Diagnostic Tests
-
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks agoHow to Monitor and Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
-

 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week agoEating for Energy: Nutritional Tips for Diabetic Health
-

 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week agoMastering Blood Sugar Control: Tips and Strategies for a Healthier Life
-
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week agoThe Importance of HbA1c Testing in Diabetes Care
-
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks agoWhat Are The Effects of Diabetes on Our Health?
-

 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week agoRadiant Skin, Healthy Living: Skincare Tips for Diabetics
-

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks agoTop Blood Glucose Monitoring Devices in 2024










