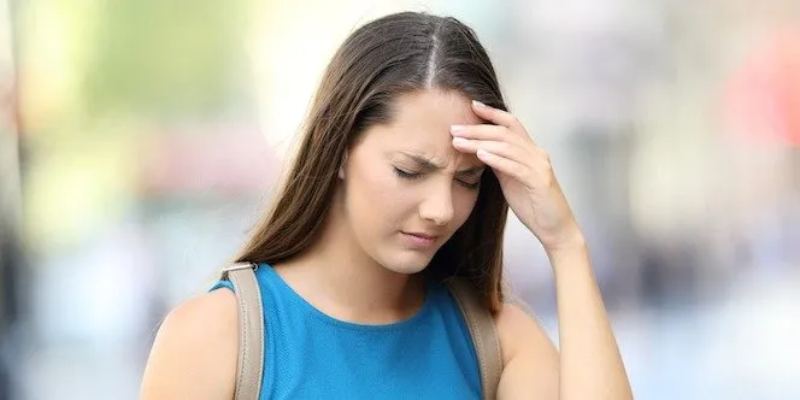
Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions globally, can sometimes develop silently. However, your body often sends subtle warning signs in the early stages. This comprehensive guide equips you to recognize these signs, understand their significance, and take proactive steps towards diagnosis and management.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Types:
- Demystifying Diabetes:
- Briefly introduce the different types of diabetes (Type 1, Type 2, Gestational) and their underlying causes.
- Focus on Type 2 diabetes, the most common form, and explain its impact on blood sugar regulation.
- The Role of Blood Sugar:
- Explain the importance of blood sugar (glucose) as a primary energy source for the body.
- Discuss how diabetes disrupts the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore:
- Urinary Frequency and Increased Thirst:
- Explain how the body attempts to eliminate excess blood sugar through increased urination.
- Describe the sensation of excessive thirst as a common symptom, often accompanying increased urination.
- Unexplained Weight Loss:
- Discuss how the body may break down muscle tissue for energy when it cannot utilize blood sugar effectively.
- Emphasize that unexplained weight loss, especially in conjunction with other symptoms, requires medical evaluation.
- Blurred Vision:
- Explain how high blood sugar can damage blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurred or cloudy vision.
- Encourage readers to schedule an eye exam if experiencing vision changes.
- Fatigue and Lack of Energy:
- Describe how the body’s inability to use glucose efficiently can lead to fatigue and a general lack of energy.
- Differentiate this from typical tiredness to emphasize the significance in diabetic individuals.
- Slow Healing Wounds and Skin Issues:
- Discuss how high blood sugar can impair circulation and slow down the healing process of wounds, cuts, or ulcers.
- Highlight the importance of seeking medical attention for any wounds that don’t heal properly.
- Frequent Infections:
- Explain how high blood sugar can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections (urinary tract infections, skin infections).
- Encourage readers to consult their doctor if they experience frequent or recurring infections.
- Numbness and Tingling in Hands and Feet:
- Describe how nerve damage, a potential complication of diabetes, can manifest as numbness, tingling, or pain in the extremities.
- Emphasize the importance of not ignoring these symptoms.
Beyond the Obvious: Atypical Symptoms of Diabetes
- Increased Hunger:
- Explain how the body may send signals of hunger even when it has enough energy due to inefficient glucose utilization.
- Encourage readers to be mindful of hunger cues and focus on eating healthy, balanced meals.
- Skin Itching and Dryness:
- Discuss how high blood sugar can contribute to dry, itchy skin.
- Recommend staying hydrated and consulting a doctor if skin problems persist.
- Yeast Infections:
- Explain how the increased presence of sugar in the body can create a favorable environment for yeast infections.
- Encourage readers to talk to their doctor for diagnosis and treatment if experiencing frequent yeast infections.
Taking Action: Early Diagnosis and Management
- The Importance of Early Detection:
- Emphasize the importance of early diagnosis for effective diabetes management and minimizing the risk of complications.
- When to See a Doctor:
- Encourage readers to seek medical advice if they experience any of the warning signs discussed, especially if symptoms are persistent.
- Diagnostic Tests:
- Briefly explain common diagnostic tests used for diabetes, such as fasting blood sugar test, HbA1c test, and oral glucose tolerance test.
- Reassure readers that these tests are simple and painless.
Living with Diabetes: A Guide to Management and Well-being
- Treatment Options:
- Briefly introduce different treatment options for diabetes, including lifestyle modifications, medications, and insulin therapy (if needed).
- Emphasize the importance of working with a healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan.
- Living a Healthy Lifestyle:
- Reiterate the importance of a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight for effective diabetes management.
- Encourage readers to explore the resources in the following section.
Disclaimer:
- Reiterate that this information is intended for general knowledge and should not replace professional medical advice.
- Encourage readers to consult with their healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis, personalized treatment plan, and ongoing management of their diabetes.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago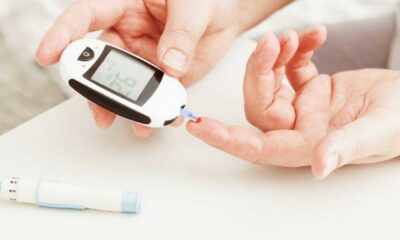
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago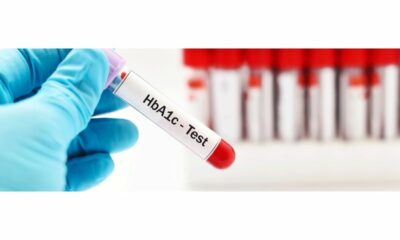
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago











