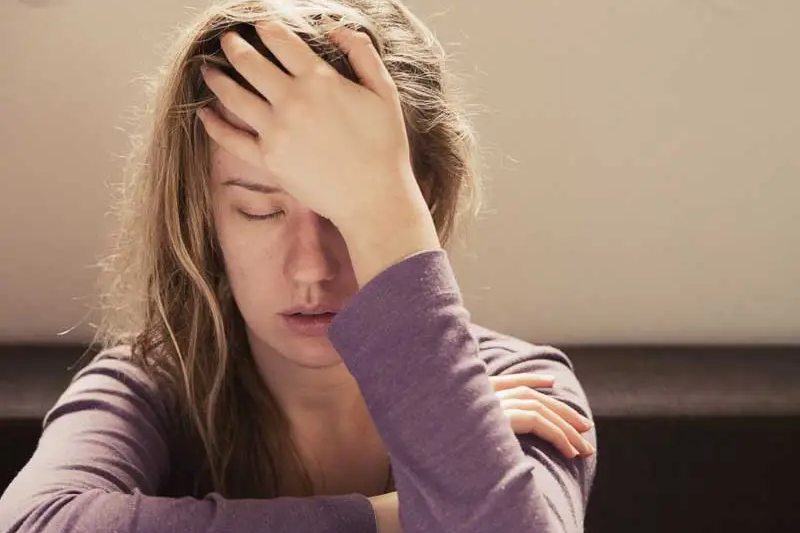
Diabetes, a group of chronic conditions affecting millions worldwide, disrupts how your body regulates blood sugar (glucose). This vital energy source fuels your cells, and uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious health complications. Early detection is crucial for effective management and preventing complications.
This article equips you to recognize the warning signs of diabetes. We’ll delve into the different types of diabetes, explore the common symptoms associated with each, and emphasize the importance of seeking medical attention if you experience any of these signs. Remember, early diagnosis and intervention are key to living a long and healthy life with or without diabetes.
Understanding the Different Types of Diabetes
Several types of diabetes exist, each with its underlying cause and symptoms:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The body produces little to no insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. Symptoms typically manifest in childhood or young adulthood, and lifelong insulin therapy is required to manage blood sugar.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common type, accounting for around 90% of all diabetes cases. In Type 2 diabetes, the body either develops insulin resistance, where cells become less responsive to insulin, or has insulin deficiency. Risk factors include family history, ethnicity, age, weight, physical inactivity, and unhealthy diet. Lifestyle modifications and medications can often help manage Type 2 diabetes effectively.
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM): This form of diabetes develops during pregnancy. Hormonal changes associated with pregnancy can affect how the body uses insulin. GDM usually resolves after childbirth but increases a woman’s risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Unveiling the Warning Signs: A Symptom Guide
The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Here’s a breakdown of common signs to watch out for:
General Symptoms:
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria): The body tries to expel excess sugar through urine, leading to increased urination, especially at night. This is one of the earliest and most common symptoms.
- Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia): Increased urination can lead to dehydration and excessive thirst, as the body tries to replenish fluids.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: The body may break down muscle and fat for energy if it can’t use glucose effectively, leading to unintended weight loss, especially in the muscles.
- Increased Hunger (Polyphagia): The body may crave more food to compensate for the lack of energy it’s getting from glucose, leading to increased hunger.
- Fatigue and Tiredness: Cells don’t have enough energy due to insufficient glucose uptake, leading to fatigue and tiredness.
Additional Symptoms:
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurred vision.
- Slow-healing wounds: High blood sugar can impair circulation and slow down the healing process of cuts, scrapes, and sores.
- Frequent infections: Diabetes can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, such as skin infections, urinary tract infections, and yeast infections.
- Itching and skin problems: High blood sugar can cause dry, itchy skin. In women, it can also lead to vaginal yeast infections.
- Fruity-smelling breath: In rare cases, uncontrolled Type 1 diabetes can lead to a buildup of ketones in the bloodstream, which can cause a fruity-smelling odor on the breath.
Recognizing Symptoms Across Different Types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Symptoms often appear quickly and can be severe, particularly excessive thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Symptoms may develop gradually and can be mild initially, making them easy to miss. However, some people with Type 2 diabetes experience no noticeable symptoms until complications arise.
- Gestational Diabetes: Symptoms are typically absent in GDM. However, some women may experience excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of diabetes is crucial for preventing serious complications. Here’s why seeking medical attention if you experience any of the warning signs is important:
- Preventing Complications: Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to various complications, including heart disease, stroke, nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney disease, eye problems (retinopathy), and foot problems. Early detection and management can significantly reduce the risk of developing these complications.
- Effective Management: Early diagnosis allows for prompt treatment and management strategies like lifestyle changes, medications, or insulin therapy to be implemented to effectively control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
- Improved Quality of Life: Early intervention and proper management can significantly improve your quality of life by reducing symptoms, preventing complications, and allowing you to maintain good overall health.
Seeking Medical Attention: What to Expect
- If you experience any of the warning signs of diabetes, it’s crucial to see your doctor for a diagnosis. Here’s what you can expect during your appointment:
- Discussion of Symptoms: Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms, including their severity and duration.
- Medical History Review: They will review your medical history, including any family history of diabetes.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may be conducted to check for signs of diabetes, such as high blood pressure or obesity.
- Blood Tests: Several blood tests are used to diagnose diabetes, including fasting blood sugar, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
Living a Healthy Life: Beyond Diagnosis
- Whether you receive a diabetes diagnosis or simply want to maintain good blood sugar control, here are some lifestyle strategies to promote overall health:
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is crucial. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. A registered dietitian can help create a personalized meal plan.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps your body use insulin more effectively and lowers blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Weight Management: If overweight or obese, losing even a modest amount of weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels helps you understand how your body reacts to food, exercise, and medications. This empowers you to adjust your management strategies accordingly.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels. Explore stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Regular Checkups: Schedule regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your blood sugar levels, assess for complications, and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
- Healthy Habits: Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as getting enough sleep, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption, can significantly benefit your overall health and diabetes management.
Conclusion
Recognizing the warning signs of diabetes is crucial for early detection and management. By understanding the different types of diabetes, their symptoms, and the importance of seeking medical attention, you can take control of your health. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. With knowledge, proactive measures, and support, you can manage diabetes effectively and live a full and healthy life.
Note:
This information is intended for general knowledge only and should not be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago