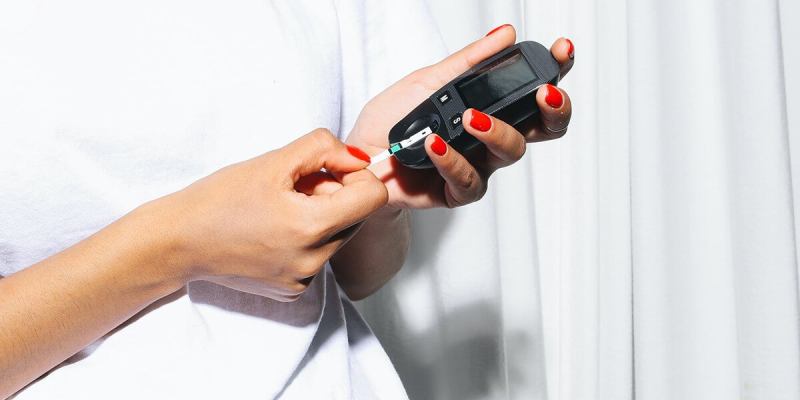
Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions of people worldwide. It disrupts the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels, leading to a variety of symptoms that can significantly impact your daily life. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of diabetes symptoms, empowering you to recognize the signs, understand their causes, and navigate the next steps towards diagnosis and management.
The Role of Blood Sugar in Our Bodies
Before exploring symptoms, let’s understand the role blood sugar plays in our health. Glucose, the primary source of energy for our cells, comes from the food we eat. The pancreas, a gland located behind your stomach, produces insulin, a hormone that acts like a key, unlocking the cells and allowing glucose to enter for energy production.
Types of Diabetes and Their Impact on Blood Sugar
There are two main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: In type 1 diabetes, the body doesn’t produce enough insulin, or stops producing it altogether. This leads to chronically high blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: In type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the cells become resistant to its effects. This also results in high blood sugar levels, although the onset may be more gradual compared to type 1 diabetes.
Unveiling the Spectrum of Diabetes Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the type of diabetes. Here’s a breakdown of some common symptoms:
- Urinary Frequency and Increased Urination (Urination): When blood sugar levels rise, the kidneys work overtime to remove excess glucose from the bloodstream. This leads to frequent urination, particularly at night.
- Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia): Frequent urination depletes fluids, leading to dehydration and intense thirst. You may find yourself constantly reaching for water, yet never feeling quite quenched.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: When the body doesn’t have enough insulin to utilize glucose for energy, it starts breaking down muscle and fat tissues for fuel. This can lead to unintentional weight loss, even if you’re eating normally.
- Increased Hunger (Polyphagia): Despite weight loss, you may experience constant hunger pangs. This is because your cells are starved for energy due to the lack of glucose entering them.
- Blurred Vision: Chronically high blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurred vision, difficulty focusing, or even vision loss if left untreated.
- Slow-Healing Wounds: High blood sugar levels impair circulation and weaken the immune system, making it harder for wounds to heal properly. Even minor cuts or scrapes may take longer to heal and be more prone to infection.
- Fatigue and Lack of Energy: When your cells are deprived of glucose, their primary energy source, it can lead to fatigue, tiredness, and a lack of energy to perform your daily activities.
- Skin Issues: Dry, itchy skin, especially around the groin area, can be a sign of high blood sugar. Diabetic neuropathy, nerve damage caused by diabetes, can also manifest as tingling or burning sensations in the hands and feet.
- Genital Yeast Infections: Frequent yeast infections in women and fungal infections in the genital area for both men and women can be linked to uncontrolled diabetes.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other medical conditions. However, experiencing any of these symptoms, especially if they occur together and persist for a while, warrants consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis.
Early Detection is Key: Recognizing the Signs of Untreated Diabetes
In some cases, diabetes can progress silently, with no noticeable symptoms in the early stages. This highlights the importance of routine health checkups, especially for those at higher risk of developing diabetes, such as individuals with a family history of the condition, those with a BMI (Body Mass Index) in the overweight or obese category, and women who have experienced gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
Beyond the Basics: Less Common Diabetes Symptoms
While the previously mentioned symptoms are more prevalent, here are some less common signs to be aware of:
- Fruity-smelling Breath: A fruity odor on the breath can be a sign of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of type 1 diabetes that occurs when the body starts breaking down fat for energy due to a lack of insulin.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can be associated with DKA or hyperglycemia (very high blood sugar).
- Shortness of Breath: Rapid, shallow breathing can be a sign of DKA.
- Confusion and Difficulty Concentrating: High blood sugar levels can affect brain function, leading to confusion and difficulty focusing.
- Numbness and Tingling: This can be a symptom of diabetic neuropathy, nerve damage caused by chronically high blood sugar levels. It typically starts in the hands and feet and can progress to other areas of the body.
- Erectile Dysfunction (Men) and Vaginal Dryness (Women): Diabetes can affect blood flow and nerve function, leading to sexual dysfunction in both men and women.
- Sleep Apnea: People with diabetes are more likely to experience sleep apnea, a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention:
- Symptoms of DKA: Fruity-smelling breath, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, confusion.
- Extreme thirst, excessive urination, and rapid weight loss: These can be signs of uncontrolled diabetes and require immediate medical intervention.
- Sudden vision changes: Blurred vision or difficulty focusing can worsen quickly if left untreated.
Diagnosis and Management of Diabetes
Early diagnosis and proper management are crucial for preventing serious complications associated with diabetes. Your doctor will likely order blood tests to measure your blood sugar levels and assess your risk for diabetes. Depending on the type and severity of your diabetes, a personalized treatment plan will be developed, which may include:
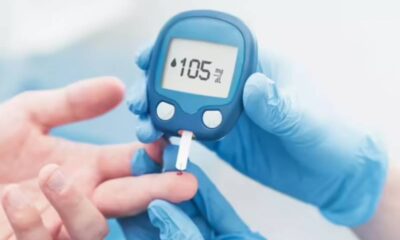
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly measuring your blood sugar levels helps you understand how your body reacts to food, exercise, and medications.
- Dietary Changes: A healthy diet plays a vital role in managing blood sugar levels. Your doctor or a registered dietitian can help you create a personalized meal plan.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps control blood sugar.
- Medications: Depending on your specific needs, medications like insulin or oral medications may be prescribed to manage blood sugar levels.
Living Well with Diabetes
Diabetes management goes beyond just controlling blood sugar. It’s about adopting a healthy lifestyle and taking proactive steps to prevent complications. Here are some additional tips:
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels. Explore stress-relieving techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Foot Care: Diabetes can increase your risk of foot problems. Inspect your feet daily for cuts, blisters, or infections, and wear proper footwear.
- Regular Checkups: Schedule regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your blood sugar levels and assess your overall health.
Knowledge Empowers Action: Embrace a Healthy Future
Understanding diabetes symptoms is the first step towards effective management. By recognizing the signs, seeking timely medical attention, and adopting healthy lifestyle changes, you can empower yourself to live a fulfilling life with diabetes. Remember, you are not alone. Utilize the wealth of resources available, connect with support groups, and take charge of your health journey!
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago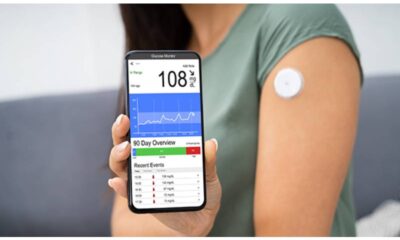
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago
 Diabetology6 hours ago
Diabetology6 hours ago
 Diabetology7 hours ago
Diabetology7 hours ago







