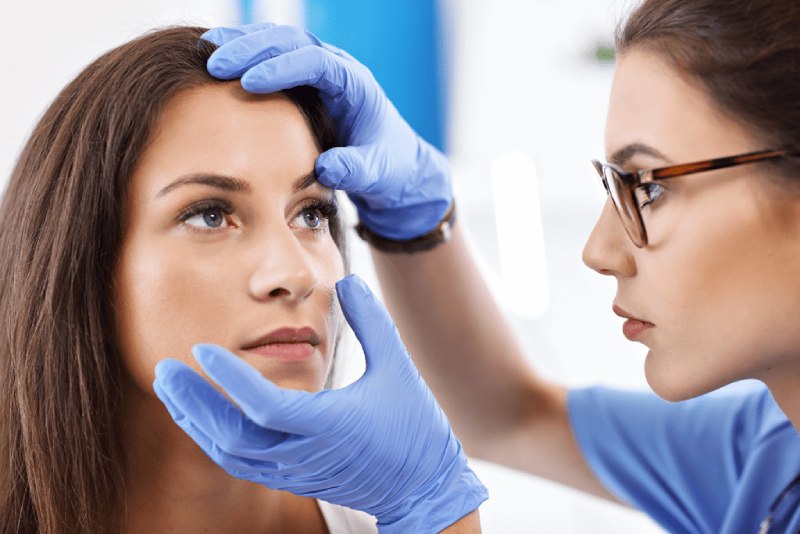
Diabetes, a chronic condition marked by elevated blood sugar levels, impacts nearly every aspect of your health, including your vision. While managing blood sugar remains paramount, regular eye exams become a crucial line of defense against sight-threatening complications. This article delves into the importance of eye exams for diabetics, exploring the silent dangers of diabetic eye diseases, the benefits of early detection, and practical tips for maintaining optimal eye health.
Why are Diabetics Particularly Susceptible to Eye Problems?
The culprit lies in high blood sugar levels. Over time, uncontrolled blood sugar damages the delicate blood vessels throughout your body, including those nourishing the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. This damage can lead to a spectrum of eye diseases, often progressing silently with minimal initial symptoms.
Here’s a closer look at the most common diabetic eye complications:
- Diabetic Retinopathy: This progressive disease weakens and damages retinal blood vessels. Early stages may show no symptoms, but as it progresses, it can cause blurry vision, floaters (seeing spots or cobwebs), and even blindness.
- Diabetic Macular Edema (DME): Fluid buildup in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp central vision, can occur due to damaged retinal blood vessels. This can lead to distorted vision, difficulty reading, and problems with color perception.
- Glaucoma: This condition, not exclusive to diabetes, increases intraocular pressure, damaging the optic nerve. While not directly caused by diabetes, diabetics have a higher risk of developing glaucoma.
- Cataracts: A clouding of the lens, the eye’s natural lens, can occur with age and is more prevalent in diabetics.
The Silent Threat: Early Detection is Key
The insidious nature of diabetic eye diseases lies in their often symptomless early stages. By the time vision changes become noticeable, significant damage may have already occurred. This is why regular eye exams are vital for early detection and timely intervention.
Here’s why early detection is crucial:
- Preserving Vision: Early diagnosis allows for prompt treatment, minimizing damage and potentially preserving vision. Treatments like laser surgery or injections can slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy and DME.
- Improved Treatment Outcomes: Early intervention leads to better treatment outcomes. Delaying treatment can significantly reduce the effectiveness of interventions and increase the risk of vision loss.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing your eye health status provides peace of mind. Regular exams allow for proactive management and a sense of control over your vision health.
Benefits of Regular Eye Exams for Diabetics
Regular eye exams for diabetics offer a multitude of benefits:
- Early Detection: Eye exams allow your ophthalmologist or optometrist to detect early signs of diabetic eye disease before symptoms arise. This enables early intervention to prevent vision loss.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: A comprehensive eye exam goes beyond just checking your vision. It includes a detailed evaluation of the retina, looking for signs of damage like bleeding or microaneurysms (weak spots in blood vessels).
- Monitoring Progression: Regular exams allow your eye doctor to monitor the progression of any existing eye disease. This helps them adjust treatment plans as needed to optimize outcomes.
- Overall Eye Health: The eye exam assesses your overall eye health, identifying other potential problems like cataracts or glaucoma, allowing for early management.
- Personalized Management Plan: Based on your eye health status, your doctor can develop a personalized management plan, including treatment recommendations and a follow-up schedule tailored to your specific needs.
What to Expect During a Diabetic Eye Exam
Diabetic eye exams are typically similar to a standard eye exam, with some additional components:
- Visual Acuity Test: Measures your ability to see at various distances.
- Dilated Eye Exam: Eye drops are used to dilate your pupils, allowing for a more comprehensive examination of the retina and other internal structures of the eye.
- Tonometry: Measures intraocular pressure to assess for glaucoma.
- Retinal Imaging: Specialized imaging techniques like fundus photography or optical coherence tomography (OCT) may be used for detailed visualization of the retina, allowing for more precise diagnosis and monitoring.
How Often Should Diabetics Have Eye Exams?
The recommended frequency of eye exams for diabetics can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Type of Diabetes: Individuals with Type 1 diabetes typically require more frequent exams than those with Type 2 diabetes.
- Duration of Diabetes: The longer you have diabetes, the higher your risk of eye complications.
- Blood Sugar Control: (Continued) More frequent exams may be recommended if your blood sugar control is suboptimal.
- Presence of Eye Disease: If you have existing diabetic eye disease, you will likely need more frequent monitoring to track its progression.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women with diabetes require additional eye exams due to the increased risk of diabetic retinopathy during pregnancy.
Here’s a general guideline for diabetic eye exam frequency:
- For individuals with well-controlled Type 2 diabetes and no signs of eye disease: An annual eye exam is recommended.
- For individuals with Type 1 diabetes or poorly controlled diabetes: More frequent exams, possibly every six months, may be advised.
- For individuals with existing diabetic eye disease: The frequency of exams will be determined by the severity of the disease and your doctor’s recommendations.
It’s crucial to discuss the recommended frequency of eye exams with your doctor based on your individual health profile.
Maintaining Optimal Eye Health with Diabetes
While regular eye exams are essential, there are additional steps you can take to safeguard your vision health:
- Manage Your Blood Sugar: Maintaining good blood sugar control through diet, exercise, and medication is the cornerstone of preventing and managing diabetic eye disease.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, combined with regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight, can contribute to overall health and potentially reduce the risk of eye complications.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking significantly increases the risk of diabetic eye disease and other health problems. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your overall health, including your vision.
- Sun Protection: Wear sunglasses that block UVA and UVB rays to protect your eyes from sun damage, which can further complicate vision problems.
- Regular Eye Care: Practice good eye hygiene by washing your hands before touching your eyes and using recommended eye drops or artificial tears if prescribed by your doctor.
Conclusion
Regular eye exams are a non-negotiable part of diabetes management. By prioritizing your vision health, you empower yourself to detect problems early, seek timely treatment, and preserve your sight for a lifetime of vibrant experiences. Embrace the power of prevention and schedule your next diabetic eye exam today.

 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago