Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions globally, disrupts how your body regulates blood sugar. While managing blood sugar levels is crucial, preventing complications is equally important. This guide equips you with knowledge and practical strategies to safeguard your health and well-being with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes Complications:
High blood sugar over time can damage various organs and systems. Here’s a breakdown of common complications and how they affect you:
- Heart Disease and Stroke: Diabetes significantly increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease (PAD). High blood sugar weakens blood vessels, promoting plaque buildup, which can narrow arteries and restrict blood flow.
- Kidney Disease: Diabetes is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Uncontrolled blood sugar damages the delicate filters in your kidneys, hindering their ability to remove waste products from your blood.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Chronic high blood sugar can damage nerves throughout your body, causing pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness. Diabetic neuropathy can affect your feet, hands, digestive system, and urinary system.
- Eye Disease: Diabetes is a leading cause of blindness in adults. It can damage blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, and glaucoma.
- Foot Problems: Nerve damage and poor circulation in the feet can lead to foot ulcers, infections, and even amputations. It’s crucial to pay close attention to foot care with diabetes.
Taking Charge: Strategies for Preventing Complications
The good news is that you have significant power to prevent or delay these complications. Here are key strategies:
This is the cornerstone of preventing complications. Work with your doctor to establish personalized blood sugar goals and a management plan. This may involve diet, exercise, medication, or a combination. Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels and make adjustments as needed.
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is essential. Limit saturated and unhealthy fats, added sugars, and processed foods. Consider consulting a registered dietitian for personalized meal plans.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Physical activity helps improve blood sugar control, reduce heart disease risk, and maintain a healthy weight.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Losing weight and maintaining a healthy body mass index (BMI) can significantly improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications.
- Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol:
High blood pressure and cholesterol further increase the risk of heart disease and stroke in people with diabetes. Work with your doctor to keep these levels under control through lifestyle changes or medication.
Smoking significantly increases the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful things you can do for your health.
Schedule regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your blood sugar levels, blood pressure, cholesterol, and for early detection of any complications.
Inspect your feet daily for cuts, blisters, or other injuries. Wash your feet daily with warm water and mild soap, dry them thoroughly, and moisturize them to prevent cracks. Wear proper-fitting shoes and avoid walking barefoot.
Get comprehensive dilated eye exams annually to detect and treat diabetic eye disease early.
Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels. Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing to manage stress effectively.
Building a Support System:
Living with diabetes can be challenging. Having a strong support system can make a significant difference. This could include:
- Family and Friends: Seek understanding and support from loved ones. Educate them about diabetes and how they can help you manage it.
- Doctor and Diabetes Care Team: Your doctor, diabetes educator, and other healthcare professionals play a crucial role in your care. Work collaboratively to establish and maintain a successful management plan.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others living with diabetes can provide valuable information, encouragement, and a sense of community.
Empowering Yourself Through Technology
Technology can be a powerful tool in managing diabetes and preventing complications. Consider these resources:
- Blood Sugar Monitoring Devices: Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and blood glucose meters provide real-time data on your blood sugar levels, allowing for adjustments to diet, medication, and activity.
- Diabetes Management Apps: Numerous apps can help you track blood sugar, carb intake, exercise, and medication. Some offer educational resources and reminders.
- Telehealth: Telehealth consultations with your doctor or diabetes educator can save time and provide convenient access to care.
Addressing Emotional Wellbeing
Living with a chronic condition like diabetes can take an emotional toll. Here’s how to prioritize your mental health:
- Recognize Signs of Depression or Anxiety: These conditions are common among people with diabetes. Symptoms include low mood, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and changes in appetite or sleep.
- Seek Help if Needed: Talk to your doctor about any emotional struggles you may be experiencing. Therapy and medication can effectively manage depression and anxiety.
- Prioritize Self-Care: Engage in activities you enjoy, get enough sleep, and practice relaxation techniques.
Healthy Habits for Long-Term Success
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Adequate sleep helps regulate hormones that impact blood sugar control.
- Dental Care: Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene are crucial for people with diabetes, as they are more susceptible to gum disease and other dental problems.
- Healthy Vaccinations: Maintain a current vaccination schedule to protect yourself from preventable infections.
- Financial Planning: Diabetes management can involve ongoing costs. Explore insurance coverage, financial assistance programs, and budgeting strategies.
Remember:
You are not alone in managing diabetes. By taking charge of your health, adopting healthy habits, and utilizing available resources, you can prevent complications and live a full and vibrant life.
Please Note:
This information is intended for general knowledge and should not be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor to create a personalized diabetes management plan.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago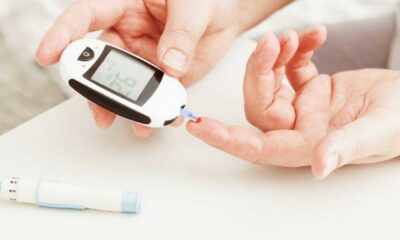
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago









