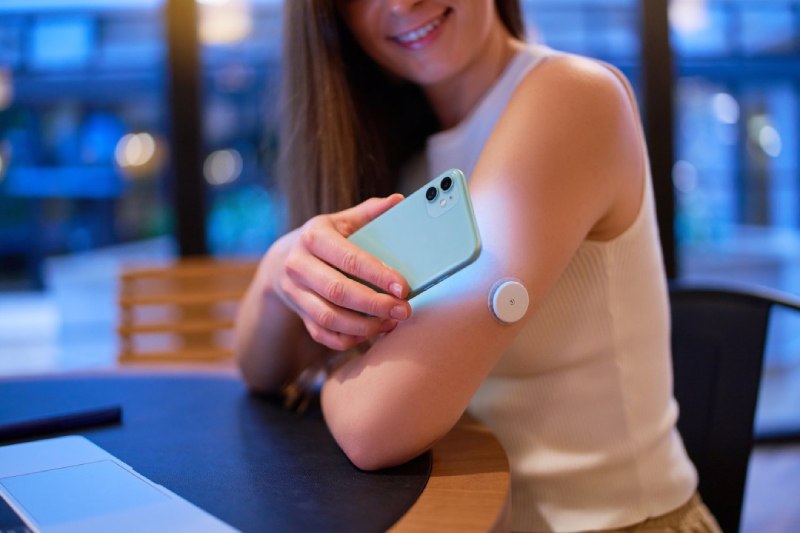
Traditionally, people with diabetes relied on finger pricking and blood glucose meters to monitor their blood sugar levels. While these methods are still valuable, advancements in technology have introduced a new era of diabetes management:
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
This comprehensive guide dives into the world of CGM, exploring its benefits, various types of CGM systems, and how to leverage this technology to optimize your diabetes management strategy.
Demystifying Blood Sugar and Its Role in Diabetes
Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary fuel source for your body’s cells. It enters cells with the help of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. In healthy individuals, blood sugar levels rise after eating and dip between meals. The pancreas releases insulin accordingly, maintaining a healthy balance.
However, in diabetes, this balance is disrupted. In type 1 diabetes, the body doesn’t produce enough insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the body either produces insufficient insulin or develops resistance to its effects. This leads to chronically high blood sugar levels, which can damage nerves, blood vessels, and organs over time.
The Revolutionary Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM systems are miniature sensor patches inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen or arm. These sensors continuously measure interstitial fluid glucose levels (the fluid between cells) every few minutes and transmit the data wirelessly to a receiver or smartphone app.
Benefits of CGM for Diabetes Management:
- Real-time Blood Sugar Trends: Unlike finger pricking, which provides a snapshot at a specific time, CGM offers a continuous picture of blood sugar fluctuations throughout the day and night.
- Improved Glycemic Control: By visualizing trends, you can identify patterns and adjust insulin doses, meal plans, and activity levels more effectively to maintain blood sugar within a healthy range.
- Reduced Hypoglycemia Risk: CGM systems often come with customizable alerts that warn you when blood sugar levels drop too low, allowing for timely intervention to prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
- Enhanced Treatment Decisions: CGM data empowers you and your healthcare provider to make informed decisions about treatment adjustments, medication dosages, and overall diabetes management strategies.
- Improved Quality of Life: By gaining better control over blood sugar levels and reducing the frequency of finger pricking, CGM can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce anxiety associated with diabetes management.
Types of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems
There are two main categories of CGM systems:
- Sensor-augmented Pump (SAP): These systems integrate CGM data with an insulin pump, allowing for automated insulin delivery based on real-time blood sugar levels.
- Standalone CGM: These systems provide real-time blood sugar data but don’t directly control insulin delivery.
Choosing the Right CGM System for You
Several factors influence CGM selection, including:
- Type of Diabetes: While both type 1 and type 2 diabetics can benefit from CGM, it’s often recommended for those requiring multiple daily injections or experiencing frequent hypoglycemic events.
- Insurance Coverage: Insurance coverage for CGM can vary. Discuss cost implications with your healthcare provider and insurance company.
- Lifestyle: Consider your daily routine and comfort level with wearing a sensor.
- Technical Skills: Evaluate your comfort level with technology and using a receiver or smartphone app to access CGM data.
Getting Started with CGM:
- Consult Your Doctor: Discuss if CGM is right for you and work with them to develop a personalized plan for using CGM data to optimize your diabetes management.
- Learn the System: Familiarize yourself with your specific CGM device and its functionalities.
- Sensor Insertion and Calibration: Learn the proper technique for sensor insertion and calibration as instructed by your healthcare provider.
- Data Interpretation: Understand how to interpret CGM data, identify trends, and use it to make informed decisions.
Optimizing Your Diabetes Management with CGM Data
Here are some key strategies to leverage CGM data for better blood sugar control:
- Identify Food Impact: Track how different meals and snacks affect your blood sugar levels and adjust your diet accordingly.
- Monitor Exercise Effects: Observe how exercise impacts your blood sugar and adjust pre-workout meals or insulin dosages if needed.
- Recognize Stress Responses: Stress can elevate blood sugar levels. Use CGM data to identify stress patterns and implement stress management techniques.
- Improved Sleep Hygiene: Poor sleep can disrupt blood sugar regulation. Utilize CGM data to assess how sleep quality impacts your blood sugar and prioritize healthy sleep habits.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Team: Share CGM data with your doctor or diabetes educator to refine your treatment plan and medication dosages.
Beyond CGM: Exploring Additional Technologies
While CGM is a game-changer, other innovative technologies are emerging to enhance diabetes management:
- Flash Glucose Monitoring (FGM): These minimally invasive sensors provide blood sugar readings with a scan, offering a less frequent snapshot compared to CGM but still valuable for trend analysis.
- Artificial Pancreas Systems (APS): These advanced closed-loop systems integrate CGM with an insulin pump and continuously adjust insulin delivery based on real-time blood sugar levels, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas.
- Smart Insulin Pens: These pens connect to smartphones and can record insulin dosages and potentially offer reminders or integrate with CGM data in the future.
Living with Diabetes: Building a Support System
Diabetes management is a lifelong journey. Here are some tips for building a strong support system:
- Connect with a Diabetes Educator: A certified diabetes educator can provide personalized education and guidance on using CGM and other tools effectively.
- Join a Support Group: Connecting with others who understand the challenges of diabetes can offer emotional support, motivation, and valuable tips.
- Open Communication with Healthcare Team: Maintain regular communication with your doctor and diabetes educator to address any concerns, questions, or adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
- Embrace Technology: Explore various diabetes management apps and online resources to track blood sugar data, calculate insulin doses, and find recipes suitable for your dietary needs.
Maintaining Motivation and Overcoming Challenges
Living with diabetes requires ongoing commitment and motivation. Here are some strategies to stay on track:
- Set Realistic Goals: Start with small, achievable goals and gradually increase the difficulty as you progress.
- Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge and reward yourself for reaching milestones, no matter how small, to maintain motivation.
- Focus on Progress, Not Perfection: There will be setbacks. Focus on the overall progress you’re making and learn from challenges.
- Prioritize Self-Care: Make time for activities you enjoy, get enough sleep, and manage stress effectively to promote overall well-being.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Ask for Help: Seek support from your healthcare team, family, and friends if you’re struggling with any aspect of diabetes management.
The Future of Diabetes Management
The future of diabetes management is bright, with continuous advancements in technology offering even more sophisticated tools for effective blood sugar control. Here’s a glimpse into what’s on the horizon:
- Improved Sensor Accuracy and Longevity: Sensor technology is constantly evolving, aiming to provide even more accurate and long-lasting readings.
- Non-invasive Glucose Monitoring: Research is ongoing for non-invasive methods to measure blood sugar levels, potentially eliminating the need for finger pricking or sensor insertion.
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-powered systems are being explored to analyze CGM data and predict blood sugar trends, allowing for even more personalized and automated insulin delivery.
- Integration with Wearable Devices: Future advancements may see seamless integration of CGM data with wearable health trackers, providing a holistic view of your health and well-being.
Conclusion
Advanced glucose monitoring tools like CGM are revolutionizing diabetes management. By leveraging CGM data and other emerging technologies, you can gain greater control over your blood sugar levels, improve your overall health, and live a fulfilling life with diabetes. Remember, you’re not alone on this journey. Embrace the support of your healthcare team, loved ones, and the ever-evolving world of diabetes management technology.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago








