Clinicians have exhibited that the normal comprehension that smothering negative considerations was not really great for your psychological well-being may not be correct, another review has shown.
Michael Anderson, a mental neuroscientist at the College of Cambridge, shared, that “a piece of the objective in psychotherapy is to recognize stifled contemplations, carry them to the very front, and address them and this is remembered to prompt improvement”.
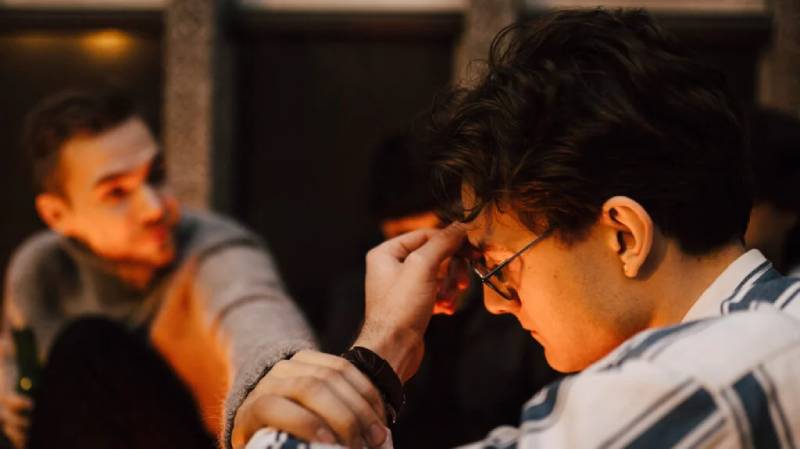
Investigations discover that stifling negative considerations seemed to lessen the probability of members psychological well-being issues demolishing after some time — Unsplash/Records
Investigations discover that stifling negative considerations seemed to lessen the probability of members’ psychological well-being issues demolishing after some time — Unsplash/Records
Clinicians have exhibited that the normal comprehension that stifling negative contemplations was not great for your psychological well-being may not be correct, another review has shown.
Michael Anderson, a mental neuroscientist at the College of Cambridge, shared, that “a piece of the objective in psychotherapy is to recognize stifled contemplations, carry them to the very front, and address them and this is remembered to prompt improvement”.
In any case, Anderson’s new examination challenges this thought, proposing a captivating other option: the demonstration of smothering negative contemplations could really yield enhancements in side effects connected with tension, gloom, and post-horrendous pressure problem (PTSD).
In a concentrate as of late distributed in the diary Science Advances, Anderson and his colleague directed research demonstrating that preparing the mind to shut out regrettable contemplations could emphatically affect emotional well-being.
Their review included 120 grown-ups from 16 unique nations, each entrusted with posting 20 feelings of trepidation in regards to future occasions, 20 expectations, and 36 impartial occasions, for example, a normal visit to the eye specialist.
Anderson made sense of, ‘The feelings of dread couldn’t be conventional, similar to ‘I’m concerned that outsiders will attack Earth.’ All things being equal, they were repeating contemplations causing trouble.’
Then, members connected a solitary word with each sort of occasion. For instance, on the off chance that somebody’s apprehension was connected with their folks falling truly sick with Coronavirus, the related word may be ‘clinic.’
A big part of the members were told to zero in on one of their negative words for a couple of moments, keeping their considerations from floating towards additional troubling thoughts. Conversely, the other half gotten a similar undertaking yet with their nonpartisan words.
Anderson explained, ‘They were told to push any wanderer contemplations insane, even momentarily, and to try not to divert themselves. Lunch ought not be on their brains.’
This exercise was rehashed 12 times each day for three days. Toward the finish of the review,
members who had shut out regrettable contemplations announced that these feelings of trepidation turned out to be less clear, and their psychological wellness had eminently worked on contrasted with the gathering entrusted with stifling unbiased considerations. These discoveries stayed steady even three months after the review’s decision.
People who at first detailed elevated degrees of uneasiness saw a momentous 44% decrease in their self-revealed stresses overall. Among those managing post-horrendous pressure, their general negative emotional well-being, as estimated by a blend of self-revealed tension, wretchedness, and stress, diminished by a normal of 16%, while their positive emotional well-being expanded by almost 10%.
Anderson commented, “Those with the most elevated characteristic tension and the most serious PTSD encountered the best advantages. Curiously, we noticed no examples of expanded negative side effects coming about because of this mediation.”
Moreover, smothering negative considerations seemed to lessen the probability of members’ emotional well-being issues deteriorating over the long haul.
90 days after the review’s decision, around 80% of members revealed that they kept on utilizing the idea concealment methods they had gotten the hang of during the review to deal with their feelings of trepidation. Anderson and his group researched whether individuals’ feelings of dread bounced back or increased however tracked down no proof to help such cases.
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology13 hours ago
Diabetology13 hours ago
 Diabetology13 hours ago
Diabetology13 hours ago