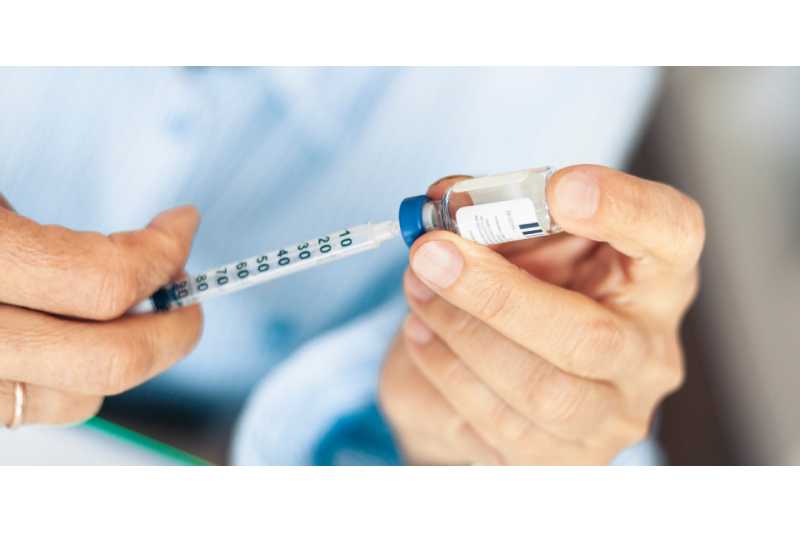
Insulin therapy is a vital treatment for people with type 1 diabetes, some individuals with type 2 diabetes, and those with gestational diabetes when blood sugar levels cannot be controlled with oral medications or lifestyle changes alone. Insulin helps the body use glucose for energy and prevents complications related to high blood sugar levels.
This guide covers the types of insulin, how it works, the best practices for administration, and tips for effective diabetes management.
What is Insulin Therapy?
Insulin therapy involves using synthetic insulin to help regulate blood sugar levels in individuals who do not produce enough insulin naturally. Insulin is typically injected under the skin or delivered through an insulin pump to ensure that glucose is properly absorbed by the body’s cells.
Who Needs Insulin Therapy?
- People with type 1 diabetes: Since the pancreas produces little to no insulin, lifelong insulin therapy is required.
- People with type 2 diabetes: Some individuals may need insulin if oral medications and lifestyle changes are not enough to control blood sugar.
- Gestational diabetes patients: In some cases, insulin is needed to regulate blood sugar during pregnancy.
- Individuals with high blood sugar emergencies: Such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS).
Types of Insulin
Insulin comes in different types based on how quickly it works and how long it lasts in the body.
1. Rapid-Acting Insulin
- Works within 15 minutes and lasts for about 3-5 hours.
- Used before meals to manage blood sugar spikes.
- Examples: Humalog, Novolog, Apidra.
2. Short-Acting Insulin (Regular Insulin)
- Takes 30-60 minutes to start working and lasts 5-8 hours.
- Used for meal-time blood sugar control.
- Examples: Humulin R, Novolin R.
3. Intermediate-Acting Insulin
- Begins working in 1-2 hours and lasts 12-18 hours.
- Used to cover blood sugar levels between meals and overnight.
- Examples: NPH (Humulin N, Novolin N).
4. Long-Acting Insulin
- Takes several hours to start working and lasts up to 24 hours.
- Provides steady blood sugar control throughout the day and night.
- Examples: Lantus, Levemir, Toujeo, Basaglar.
5. Ultra-Long-Acting Insulin
- Works for 36+ hours with no peak.
- Used for continuous blood sugar control.
- Examples: Tresiba.
Methods of Insulin Administration
- Insulin Injections: The most common method using a syringe or insulin pen.
- Insulin Pumps: Delivers insulin continuously throughout the day.
- Inhaled Insulin: A newer option for those who prefer an alternative to injections.
- Insulin Jet Injectors: Uses high-pressure air to deliver insulin without needles.
How to Use Insulin Safely
- Follow your doctor’s prescription for insulin dosage and timing.
- Rotate injection sites (abdomen, thighs, arms) to avoid skin thickening.
- Store insulin properly in the refrigerator but avoid freezing.
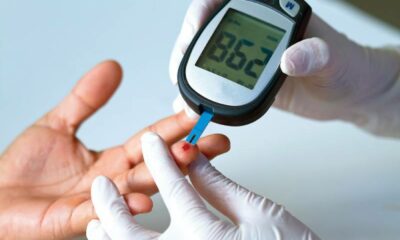
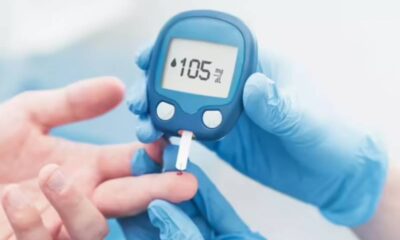
- Monitor blood sugar regularly to adjust insulin doses as needed.
- Be aware of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) symptoms like dizziness, sweating, and shakiness.
Managing Insulin Therapy with Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy eating: Follow a balanced diet with low-glycemic foods.
- Regular exercise: Helps insulin work more effectively.
- Stress management: Reduces unnecessary blood sugar fluctuations.
- Routine check-ups: Ensure proper insulin effectiveness and adjustments as needed.
Common Side Effects of Insulin Therapy
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) due to too much insulin.
- Weight gain as insulin helps the body store glucose.
- Injection site reactions like redness or swelling.
Final Thoughts
Insulin therapy plays a crucial role in diabetes management, allowing individuals to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Understanding how insulin works, the different types available, and the best administration methods can help patients use insulin effectively and improve their overall quality of life.
For a personalized insulin plan, consult a healthcare provider to ensure the best approach to managing diabetes.
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology12 hours ago
Diabetology12 hours ago
 Diabetology13 hours ago
Diabetology13 hours ago