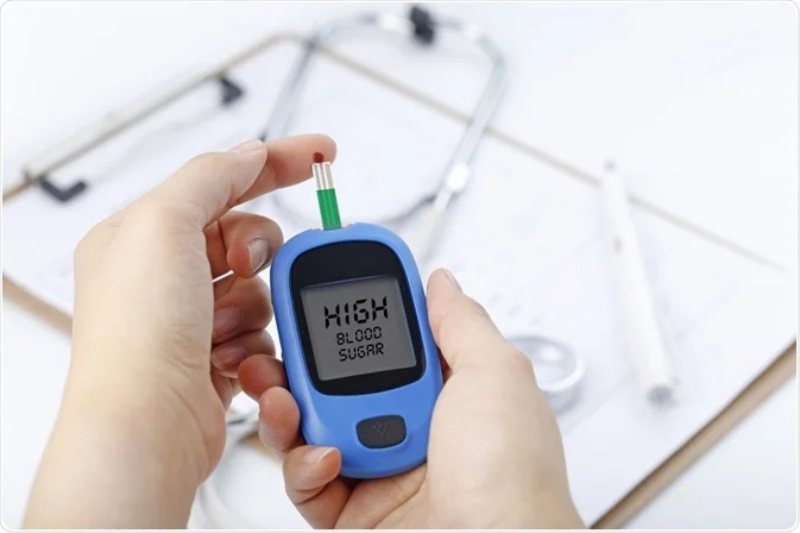
Uncontrolled high blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, can be a cause for concern. This guide empowers you to understand the root causes of high blood sugar and equips you with effective prevention strategies. By taking charge of your health, you can maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing diabetes and other chronic health conditions.
Understanding Blood Sugar: The Body’s Energy Source
- The Role of Glucose:
- Briefly introduce glucose (sugar) as the primary source of energy for our cells.
- Explain how the body absorbs glucose from the bloodstream after we eat carbohydrates.
- The Importance of Insulin:
- Introduce insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, as the key player in regulating blood sugar levels.
- Explain how insulin unlocks cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy.
Demystifying High Blood Sugar: When Your System Loses Balance
- Insulin Resistance:
- Explain insulin resistance, a condition where cells become less responsive to insulin’s signal, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Discuss potential contributors to insulin resistance, such as obesity, physical inactivity, and certain medications.
- Insufficient Insulin Production:
- Briefly discuss type 1 diabetes as a condition where the body produces little or no insulin, leading to high blood sugar.
- Other Factors Contributing to High Blood Sugar:
- Briefly mention other factors that can elevate blood sugar, such as stress, illness, hormonal changes, and certain medications.
Identifying the Culprits: Common Causes of High Blood Sugar
- Dietary Choices:
- Discuss how refined carbohydrates (sugary drinks, white bread, pastries) are quickly broken down into glucose, causing blood sugar spikes.
- Encourage readers to choose whole grains, fruits with a lower glycemic index (GI), and limit added sugar intake.
- Physical Inactivity:
- Explain how regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps the body utilize glucose more efficiently.
- Encourage readers to incorporate physical activity into their daily routine, even small changes can make a difference.
- Being Overweight or Obese:
- Briefly discuss how excess body fat can contribute to insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels.
- Stress:
- Explain how chronic stress can elevate stress hormones, impacting insulin sensitivity and increasing blood sugar levels.
- Encourage stress management techniques such as mindfulness exercises or yoga.
- Age:
- Briefly mention the natural decline in insulin production and increased risk of insulin resistance with age.
Taking Control: Effective Strategies to Prevent High Blood Sugar
- Embrace a Balanced Diet:
- Emphasize the importance of a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Encourage mindful eating practices like portion control and reading food labels.
- Move Your Body Regularly:
- Discuss the benefits of incorporating physical activity into your daily routine, aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Encourage finding activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or dancing.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Discuss the benefits of weight management for improving insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
- Encourage readers to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized weight management strategies.
- Manage Stress Effectively:
- Introduce healthy stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time in nature.
- Encourage readers to identify and address personal stressors.
- Regular Health Screenings:
- Highlight the importance of regular checkups with your doctor to monitor blood sugar levels and identify any potential problems early on.
Additional Tips for Blood Sugar Balance:
- Adequate Sleep:
- Briefly discuss how sleep deprivation can disrupt hormones and potentially contribute to blood sugar irregularities.
- Encourage aiming for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Explain how staying hydrated helps the body function optimally and may indirectly improve blood sugar control.
- Encourage readers to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Consider Supplements (Consult Doctor First):
- Briefly discuss certain supplements like chromium or berberine that may offer potential blood sugar benefits, but emphasize consulting a doctor before taking any supplements.
Living with Prediabetes: A Window of Opportunity
- Understanding Prediabetes:
- Briefly explain prediabetes as a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough for a type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
- The Importance of Early Intervention:
- Emphasize the importance of early intervention with lifestyle changes to prevent or delay the progression to type 2 diabetes.
Beyond Prevention: Managing High Blood Sugar if Present
- Treatment Options for High Blood Sugar:
- Briefly discuss potential treatment options for high blood sugar, such as medications, depending on the underlying cause and severity.
- Emphasize the importance of working with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan.
- The Role of Self-Monitoring:
- Highlight the importance of self-monitoring blood sugar levels at home for individuals with diabetes or prediabetes.
- This allows for adjustments in diet, medication, or activity as needed.
Building a Support System: Resources and Encouragement
- Online Resources:
- Provide a list of reputable online resources for learning more about blood sugar management, including websites of diabetes organizations and government health agencies.
- Support Groups:
- Encourage connecting with support groups for people with prediabetes or diabetes.
- These groups can provide valuable information, motivation, and a sense of community.
- Healthcare Professionals:
- Emphasize the importance of working closely with a healthcare team, including doctors, registered dietitians, and diabetes educators, for ongoing support and personalized guidance.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Health
By understanding the causes of high blood sugar and adopting preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes and other chronic health conditions. Remember, even small changes in your diet, activity level, and stress management can have a powerful impact on your blood sugar control and overall well-being. This guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to take charge of your health and create a path towards a healthier future.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago