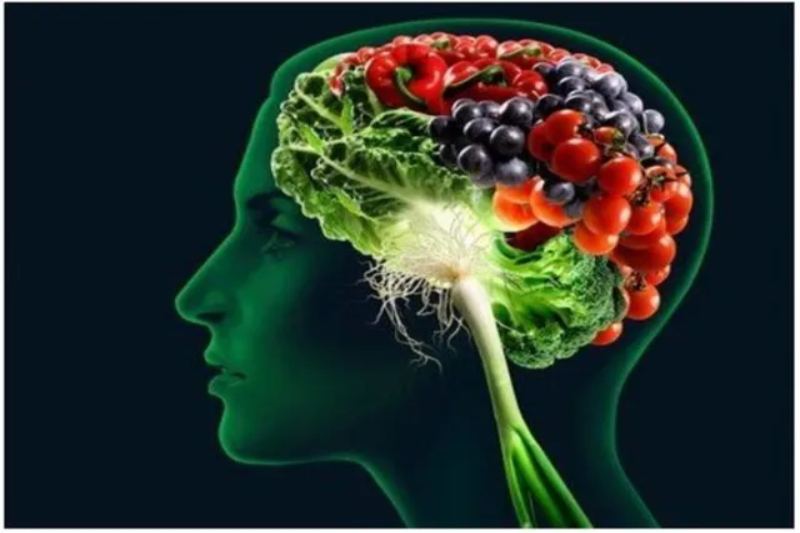
Nutrition and Mental Health
The UK Biobank, a sizable database holding health and lifestyle data from hundreds of thousands of people, was accessed by the researchers. The research team integrated a multitude of objective health data with in-depth food surveys, such as:
- Blood tests: These show blood sugar and cholesterol levels, two metabolic markers that are altered by food.
- Brain scans: These pictures shed light on the composition of the brain and any alterations that may be brought about by dietary or other health-related variables.
- Genetic testing: This examines a person’s DNA to identify genetic variants that may impact dietary choices or the body’s absorption of specific nutrients.
- Assessments of mental well-being: Participants answered questions about their general mental health, anxiety, and mood.
- Cognitive tests: Participants completed assessments meant to gauge their capacity for memory, attention, problem-solving skills, and other mental processes.
- The goal of the researchers’ analysis of all this data was to identify consistent patterns connecting dietary decisions to different facets of physical and mental health by employing cutting-edge computer technologies.
Diet Affects The Anatomy and Mental Health Of The Brain
The results of the study clearly imply that maintaining a healthy diet is important for brain health. Individuals that prioritized whole foods in their diets, such as fruits, vegetables, seafood, and lean protein, demonstrated a number of important benefits:
- Better mental health: There was a lower likelihood of anxiety and depressive symptoms in these people. Consuming a balanced diet may affect the way brain chemicals that control mood and stress are produced.
- Improved cognitive function: Higher scores on tests of memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities were associated with a healthy diet. This shows that the nutrients present in whole foods assist the brain’s efficient information processing.
- Greater amounts of gray matter: Gray matter is a form of brain tissue that is densely populated with nerve cells that are necessary for cognition, learning, and making decisions. A balanced diet was associated with greater gray matter, which may have an effect on cognitive function and general intelligence.
Reasons To Gradually Modify Your Diet
The researchers emphasize that there is little chance that restricted eating regimens or fad diets can improve brain function in the long run. Rather, they advise concentrating on making long-lasting adjustments that you can stick with.
Modest, steady changes, such as gradually reducing added sugar or excessively processed fats, can have a significant effect. There are a few benefits to this strategy:
- Decreased cravings: Your body has time to adjust when you make little changes, which may lessen intense cravings for unhealthy foods.
- Change in natural preferences: Your taste buds may change as you gradually introduce more whole foods, making healthy selections seem more enticing and pleasurable.
- Habit formation: Compared to making big, willpower-based adjustments that frequently turn out to be unsustainable over time, tiny, regular alterations have a greater chance of becoming lasting habits.
Socioeconomic, Environmental, and Genetic Aspects
- The study emphasizes how complexly nature and nurture interact. Although genetics can affect our eating preferences, having access to a good diet is equally significant.
“Since dietary choices can be influenced by socioeconomic status, it’s crucial to ensure that this does not hinder individuals from adopting a healthy balanced dietary profile,” noted Professor Jianfeng Feng, the study’s lead author.
The study emphasizes how food policy has the power to influence public health. Governments have a part to play in ensuring that everyone has access to and can afford wholesome options. More personally, families and schools have a critical role in fostering good eating habits in children from an early age.
Dietary Significance For The Brain
Even though this study offers strong evidence about the connection between diet and brain health, it’s crucial to keep in mind that this is still an intricate and developing area of study. There is still a lot to discover. An area of great interest for scientists now under investigation is the function of the gut microbiome.
Trillions of bacteria reside in our digestive tract and are collectively referred to as the gut microbiome. These microorganisms are essential for immunological and digestive processes. Scientists are finding new ways in which the microorganisms in our stomachs interact with our brains.
Dietary changes that impact the makeup of our gut microbiome may have an impact on our mood and cognitive performance.
Researchers are looking at how a good diet supports a healthy gut flora, which may have advantageous effects on our brains. These findings may pave the way for innovative and exciting new strategies to support cognitive health and mental well-being.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
















