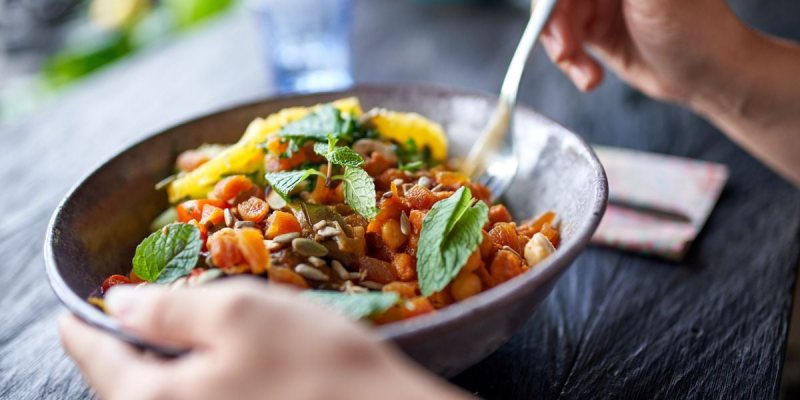
Diabetes may require dietary adjustments, but it doesn’t mean sacrificing flavor or enjoyment. This comprehensive guide empowers you to discover a world of delicious and nutritious foods that support effective diabetes management. Through informed choices, you can create a balanced and fulfilling diet that fuels your body and optimizes your well-being.
Understanding Blood Sugar and Food Choices
- The Role of Blood Sugar:
- Briefly introduce the concept of blood sugar (glucose) as the primary energy source for cells.
- Explain how diabetes disrupts the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- The Glycemic Index (GI):
- Introduce the concept of the glycemic index (GI) and its impact on blood sugar levels.
- Explain how low-GI foods release sugar slowly into the bloodstream, promoting better blood sugar control.
- Building a Balanced Plate:
- Introduce the concept of a balanced plate model, emphasizing portion control and incorporating various food groups.
- Encourage readers to fill half their plate with non-starchy vegetables (low GI), followed by lean protein and whole grains.
Nutritional Powerhouses: Best Food Choices for Diabetics
- Non-Starchy Vegetables:
- Highlight the importance of non-starchy vegetables as a cornerstone of a diabetic diet due to their low GI, fiber content, and essential vitamins and minerals.
- Provide examples of a variety of non-starchy vegetables (broccoli, spinach, leafy greens, etc.) and offer tips for incorporating them into every meal.
- Fiber-Rich Fruits:
- Discuss the importance of fiber in slowing down sugar absorption and promoting satiety.
- Recommend fruits with a lower GI, such as berries, apples, pears, and grapefruit, and suggest portion control strategies.
- Whole Grains:
- Explain the benefits of whole grains over refined grains due to their higher fiber content and slower impact on blood sugar.
- Offer examples of whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, whole-wheat bread, etc.) and suggest incorporating them throughout the day.
- Lean Protein Sources:
- Discuss the importance of protein for building and maintaining muscle mass, promoting satiety, and managing blood sugar.
- Recommend lean protein sources like fish, poultry, beans, lentils, and tofu, and offer healthy preparation methods.
- Healthy Fats:
- Differentiate between healthy and unhealthy fats.
- Encourage consuming healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish, which contribute to satiety and heart health.
- Emphasize moderation and mindful portion control.
Foods to Limit or Avoid:
- Sugary Drinks and Processed Foods:
- Explain how sugary drinks and processed foods are often high in added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats, leading to blood sugar spikes.
- Encourage readers to limit or avoid these foods and suggest healthier alternatives (water, unsweetened tea/coffee, whole fruits).
- Red Meat and Processed Meats:
- Discuss the potential link between excessive red meat consumption and increased risk of diabetes complications.
- Encourage readers to limit red meat intake, choose lean cuts when consumed, and explore alternative protein sources like fish or plant-based proteins.
- Refined Grains:
- Explain how refined grains like white bread, pasta, and pastries are quickly broken down into sugar, causing blood sugar spikes.
- Encourage opting for whole grains whenever possible for sustained energy and better blood sugar control.
Beyond the Basics: Meal Planning and Recipe Inspiration
- Meal Planning Strategies:
- Offer practical tips for creating a personalized meal plan that considers dietary needs, preferences, and lifestyle.
- Encourage readers to plan meals in advance, shop with a grocery list, and prepare healthy snacks to avoid unhealthy choices on the go.
- Delicious Diabetic-Friendly Recipes:
- Include a variety of delicious and easy-to-follow recipes for breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks, featuring the best foods for diabetes management.
- Cater to different dietary preferences (vegetarian, gluten-free) and cooking styles to keep mealtimes exciting.
Lifestyle Habits for Enhanced Blood Sugar Control
- Portion Control:
- Emphasize the importance of portion control for managing blood sugar levels.
- Offer tips for estimating portion sizes, using smaller plates, and reading food labels to understand serving recommendations.
- Mindful Eating:
- Discuss the benefits of mindful eating practices like paying attention to hunger cues, savoring each bite, and avoiding distractions during meals.
- Encourage readers to slow down while eating, listen to their body’s signals, and avoid emotional eating.
- Regular Physical Activity:
- Briefly discuss how regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps manage blood sugar levels.
- Encourage readers to find activities they enjoy and incorporate movement throughout the day.
Living with Diabetes: A Supportive Community
- The Importance of Social Support:
- Discuss the value of social support for managing diabetes and maintaining healthy lifestyle changes.
- Encourage connecting with family, friends, or joining online communities for support and motivation.
- Working with a Registered Dietitian:
- Highlight the benefits of consulting a registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice and meal planning strategies tailored to individual needs and preferences.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Approach to Healthy Living
By embracing a balanced and delicious diabetic diet, you can empower yourself to manage your blood sugar effectively and live a fulfilling life. Remember, healthy eating is a journey, not a destination. Focus on progress, not perfection, and celebrate your achievements along the way.
Disclaimer:
- Reiterate that this information is intended for general knowledge and should not replace professional medical advice.
- Encourage readers to consult with their healthcare provider for a personalized dietary plan based on their individual health status, medication use, and treatment goals.
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology1 day ago
Diabetology1 day ago
 Diabetology1 day ago
Diabetology1 day ago