Sugar diabetes, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a chronic condition characterized by persistently high blood sugar levels. While diabetes can sometimes have no noticeable symptoms in the early stages, early detection is crucial for effective management and preventing complications.
This comprehensive guide empowers you to recognize the signs and symptoms of sugar diabetes, understand the importance of early detection, and take proactive steps to safeguard your health.
Understanding Blood Sugar and the Role of Insulin
Before diving into symptoms, let’s establish a foundation. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for our cells. The body naturally regulates blood sugar levels through a complex interplay of hormones, primarily insulin and glucagon:
- Insulin: Produced by the pancreas, insulin acts like a key, unlocking the doors of cells and allowing glucose to enter for energy production.
- Glucagon: Also produced by the pancreas, glucagon acts like the opposite of insulin, raising blood sugar levels when they fall too low.
In diabetes, this delicate balance is disrupted, leading to chronically high blood sugar levels.
Why Early Detection Matters: The Power of Proactive Management
Early detection of diabetes is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevent Complications: Chronically high blood sugar levels can damage nerves, blood vessels, and organs over time. Early detection and effective management can significantly reduce the risk of complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and nerve damage.
- Improved Treatment Outcomes: Early intervention allows for starting treatment plans sooner, leading to better blood sugar control and overall health outcomes.
- Lifestyle Changes Make a Difference: Catching diabetes early allows for lifestyle modifications like diet changes and increased physical activity to have a more significant impact on managing blood sugar levels and potentially preventing the need for medications.
- Peace of Mind: Early diagnosis and proactive management can alleviate anxiety and empower you to take control of your health.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Sugar Diabetes
While symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of diabetes, here are some key signs to watch out for:
Urinary Symptoms:
- Increased urination (polyuria): High blood sugar levels can cause the kidneys to work overtime to filter excess glucose, leading to frequent urination, especially at night.
Excessive Thirst (polydipsia):
- Frequent urination can lead to dehydration, triggering the body’s thirst mechanism to replenish fluids.
Unintended Weight Loss:
- The body may start breaking down muscle and tissue for energy when it can’t access glucose effectively due to insulin resistance or deficiency.
Increased Hunger (polyphagia):
- The body may sense a lack of energy due to cells not being able to utilize glucose properly, leading to increased hunger.
Blurred Vision:
- High blood sugar levels can affect the lenses in the eyes, causing blurred vision.
Fatigue and Lack of Energy:
- Cells deprived of glucose, their primary energy source, can lead to fatigue and a general lack of energy.
Slow-Healing Wounds and Skin Infections:
- High blood sugar levels can impair the immune system’s ability to fight infections, leading to slow-healing wounds and an increased risk of skin infections.
Numbness or Tingling in the Hands or Feet (Neuropathy):
- High blood sugar can damage nerves, causing numbness or tingling sensations in the extremities.
It’s important to note: These symptoms can also be caused by other medical conditions. However, if you experience any of these signs, especially if they occur together or worsen over time, schedule an appointment with your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Taking Action: Early Detection and Management Strategies
If you suspect you might have diabetes, don’t hesitate to see your doctor. Early diagnosis can be made through simple blood tests:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures your blood sugar level after not eating for at least 8 hours.
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test: Provides an average picture of your blood sugar control over the past 2-3 months.
Depending on the diagnosis, your doctor will discuss personalized management strategies. These may include:
- Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for managing blood sugar levels.
- Medications: Depending on the type and severity of diabetes, medications like oral medications or insulin injections may be prescribed.
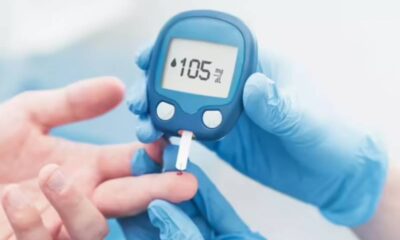
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels with a glucometer helps you understand how food, exercise, and medications affect your blood sugar. This empowers you to make informed decisions about your diabetes management.
- Education and Support: Learning about diabetes empowers you to take charge of your health. Numerous resources are available, including online resources, support groups, and diabetes educators.
- Working with Your Healthcare Team: Building a strong relationship with your doctor, diabetes educator, and other healthcare professionals is vital for comprehensive diabetes management. Regular checkups allow for monitoring your progress, adjusting treatment plans as needed, and addressing any concerns you may have.
Remember: Early detection and effective management are key to living a long and healthy life with diabetes. By being proactive, you can take control of your health and prevent complications.
Living Well with Diabetes: A Holistic Approach
While managing blood sugar is crucial, diabetes management extends beyond that. Here’s how to create a holistic approach to living well with diabetes:
- Emotional Well-being: Living with a chronic condition can be emotionally challenging. Address stress through relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Healthy Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate blood sugar.
- Preventative Care: Schedule regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your blood sugar levels, screen for complications, and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
- Support System: Connect with a diabetes support group or find a healthcare team that specializes in diabetes management. Having a support system can make a significant difference in your overall well-being.
Conclusion:
Sugar diabetes, though a chronic condition, doesn’t have to define your life. By recognizing the early signs and symptoms, seeking prompt diagnosis, and implementing effective management strategies, you can take control of your health and live a fulfilling life. Remember, early detection is crucial. Don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with your doctor if you experience any concerning symptoms. With proactive management and a holistic approach to your well-being, you can empower yourself to live a healthy and active life.
Disclaimer:
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor for personalized guidance on managing your diabetes.
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago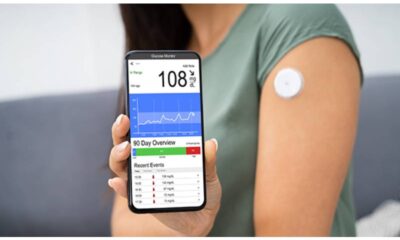
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology12 hours ago
Diabetology12 hours ago
 Diabetology13 hours ago
Diabetology13 hours ago











