In the ever-evolving world of diabetes management, technology plays a transformative role. This comprehensive guide explores various technological advancements that empower individuals with diabetes to effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Understanding the Benefits of Diabetes Technology
Diabetes technology offers a multitude of benefits, including:
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Technology enables more precise blood sugar monitoring and facilitates adjustments in diet, medication, or insulin therapy for optimal control.
- Enhanced Self-Management: Technological tools empower individuals with diabetes to take a more active role in managing their condition, fostering independence and self-efficacy.
- Convenience and Flexibility: Technology streamlines tasks like data tracking and communication with healthcare providers, offering greater convenience and flexibility in managing diabetes.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Effective blood sugar control achieved through technology can significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes.
- Improved Quality of Life: Technology can alleviate the burden of diabetes management, allowing individuals to focus on living a healthy and fulfilling life.
Blood Sugar Monitoring: The Foundation of Technology
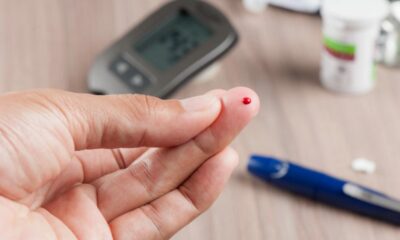
Accurate blood sugar monitoring is the cornerstone of effective diabetes management. Here are some key technological advancements in this area:
- Blood Glucose Meters: These traditional devices use a finger prick to draw a drop of blood and measure glucose levels. While convenient and portable, they require frequent finger pricks, which can be inconvenient for some users.
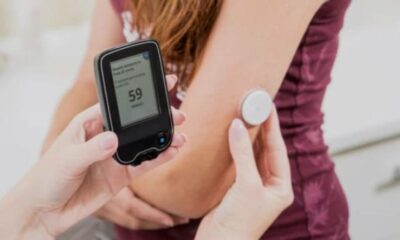
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): These innovative devices use a sensor inserted under the skin to provide real-time blood sugar data throughout the day and night. CGMs offer a more comprehensive picture of blood sugar trends and fluctuations, allowing for proactive adjustments in management.
- Non-invasive Blood Sugar Monitoring: Research is ongoing in developing non-invasive methods for blood sugar monitoring, such as devices using sensors worn on the arm or analyzed through tears or sweat. These advancements aim to eliminate the need for finger pricks altogether.
Insulin Delivery Systems: Tailoring Insulin Therapy
For individuals with type 1 diabetes and some type 2 diabetes cases, insulin therapy is essential for managing blood sugar levels. Technology offers various options for insulin delivery:
- Multiple Daily Injections (MDI): This traditional method involves injecting insulin using pens or syringes multiple times a day. While still effective, it requires discipline and accurate dosing.
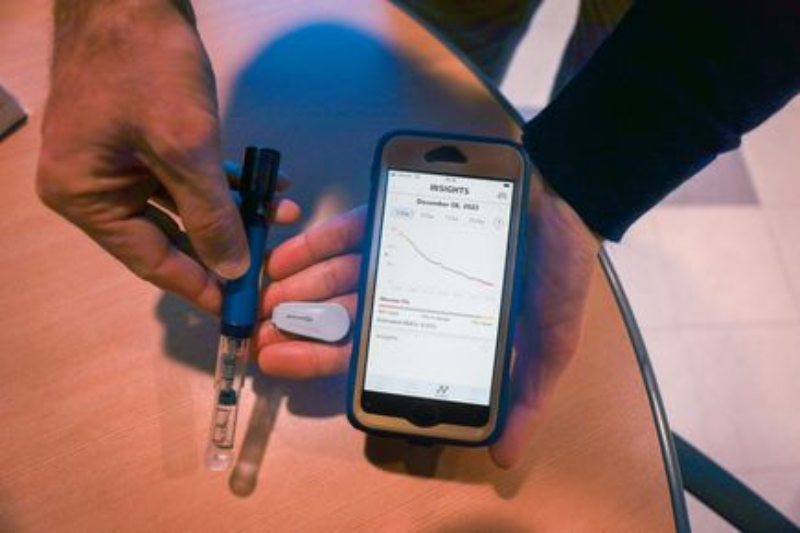
- Insulin Pumps: These computerized devices deliver insulin subcutaneously in a continuous or programmed manner. They offer greater flexibility and precision compared to MDI therapy.
- Automated Insulin Delivery Systems (Closed-Loop Systems): These advanced systems integrate CGMs with insulin pumps to create a closed-loop system. The CGM data is used to automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time blood sugar levels, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas. This technology offers optimal blood sugar control and reduces the burden of constant monitoring and adjustments.
Data Management and Analytics
Modern diabetes technology generates a wealth of data, including blood sugar readings, insulin doses, food intake, and exercise logs. Effective data management and analysis tools are crucial to:
- Identify Trends: Analyze data to identify patterns in blood sugar fluctuations and factors that influence them.
- Personalize Management: Use data insights to personalize your diabetes management plan, tailoring diet, exercise, and medication regimens for optimal results.
- Improve Decision-Making: Data analysis empowers informed decision-making regarding real-time adjustments and long-term management strategies.
- Communication with Healthcare Teams: Sharing data with your healthcare team allows for collaborative adjustments and optimized diabetes care.
There are various data management tools available, including diabetes management apps, cloud-based platforms offered by device manufacturers, and healthcare provider portals.
Emerging Technologies on the Horizon
The future of diabetes technology holds exciting possibilities:
- Artificial Pancreas Systems: Advancements in closed-loop systems will offer even greater automation and personalization in insulin delivery, further simplifying and optimizing diabetes management.
- Smart Insulin Pens: These next-generation pens might integrate with CGMs and communicate data for better insulin dosing decisions.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring: Remote consultations with healthcare providers using telehealth platforms can be more convenient and accessible for managing diabetes.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors with Remote Monitoring: Future CGMs might allow for real-time data sharing with healthcare providers, enabling proactive intervention if needed.
- Bioartificial Pancreas: Research is exploring the potential of implanting bioartificial pancreas devices that mimic the function of a healthy pancreas, offering a potential long-term solution for insulin production.
Considerations and Challenges
While diabetes technology offers significant benefits, there are also some considerations and challenges:
- Cost: Advanced diabetes technology can be expensive, and insurance coverage might vary.
- Access: Not everyone may have equal access to technology due to cost, geographic location, or technological literacy. Addressing these disparities is crucial for ensuring equitable healthcare access.
- User Training and Support: Utilizing advanced technology effectively requires proper training and ongoing support. Healthcare providers and device manufacturers need to provide comprehensive resources to empower users.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: Data security and privacy are paramount when using various diabetes technology platforms. Ensuring robust security measures is essential.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals with Diabetes
Diabetes technology is revolutionizing diabetes management, offering individuals greater control, flexibility, and improved quality of life. As technology continues to evolve, the future promises even more sophisticated tools to simplify and optimize diabetes care. By embracing these advancements, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition and live fulfilling lives.
Here are some additional points to consider:
- Importance of Individualized Care: Technology should complement, not replace, personalized diabetes management plans created in collaboration with healthcare professionals.
- Focus on Holistic Wellness: While technology plays a crucial role, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management remains essential.
- The Power of Community: Connect with diabetes support groups or online communities to share experiences, learn from others, and access valuable resources.
Embrace the power of technology to navigate your diabetes journey with greater confidence and well-being!
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge and should not be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor to determine the most appropriate diabetes management technology for your individual needs.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago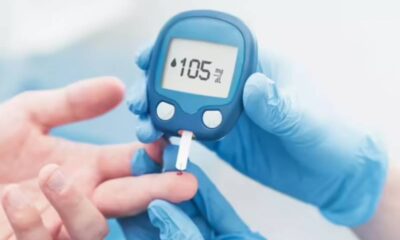
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago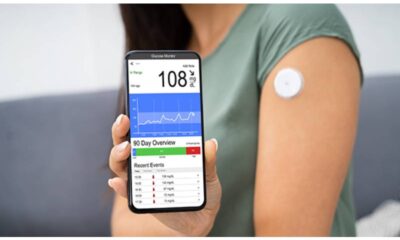
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago