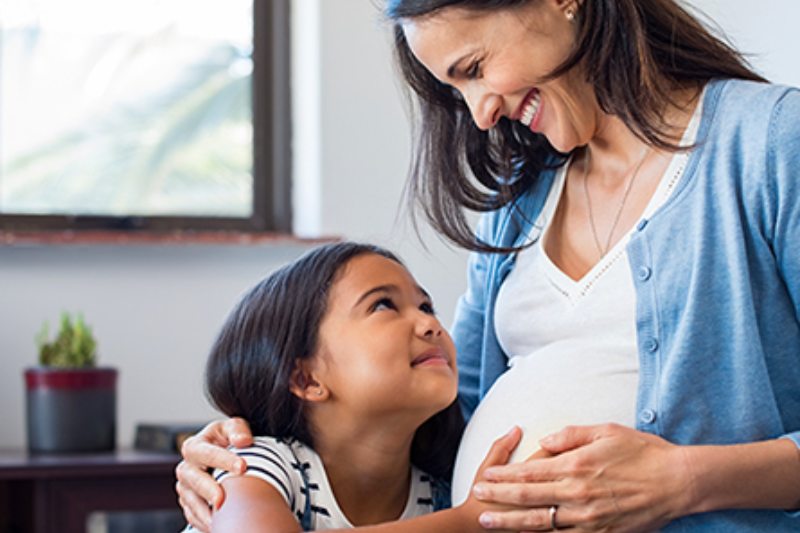
The journey of pregnancy is a transformative experience, and for women with diabetes, it requires extra planning and careful management. This guide empowers women with pre-existing diabetes or gestational diabetes to navigate pregnancy with confidence and ensure the well-being of both mother and baby.
Understanding the Types of Diabetes and Pregnancy
There are two main scenarios when diabetes and pregnancy intersect:
- Pre-existing Diabetes (Type 1 or Type 2): Women with diagnosed diabetes before pregnancy require meticulous management to maintain optimal blood sugar control throughout pregnancy.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type of diabetes develops during pregnancy when the body struggles to produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects. Gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth but increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Planning for a Healthy Pregnancy
If you have diabetes, planning for pregnancy is crucial. Here are some key steps:
- Preconception Consultation: Consult your doctor before conception to discuss your diabetes management plan, potential risks, and medication adjustments if needed.
- Achieving Optimal Blood Sugar Control: Focus on maintaining blood sugar levels within the recommended range before pregnancy. This significantly reduces the risk of complications for both mother and baby.
- Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Prioritize regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and healthy weight management before and during pregnancy.
Optimizing Diabetes Management During Pregnancy
Maintaining optimal blood sugar control throughout pregnancy is critical. Here’s how to achieve this:
- Close Collaboration with Your Healthcare Team: Work closely with your doctor, diabetes educator, and other healthcare professionals to create a personalized pregnancy management plan.
- Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: Frequent blood sugar monitoring, using finger pricks or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) if recommended by your doctor, allows for adjustments in diet, medication, or insulin therapy as needed.
- Dietary Adjustments: A balanced and well-planned diet is essential. Focus on whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Work with a registered dietitian to create a pregnancy-safe meal plan that helps manage blood sugar levels.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining blood sugar control and overall health during pregnancy. Choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga, with your doctor’s approval.
- Medication Adjustments: Your doctor may adjust your diabetes medications or prescribe insulin therapy to ensure optimal blood sugar control throughout pregnancy.
Potential Complications and Early Detection
While proper management can significantly reduce risks, diabetes can sometimes lead to complications during pregnancy. Here’s what to watch for:
- Birth Defects: High blood sugar levels in early pregnancy can increase the risk of certain birth defects. Maintaining optimal blood sugar control before and during pregnancy is crucial.
- Miscarriage and Stillbirth: Uncontrolled diabetes can increase the risk of miscarriage or stillbirth.
- Macrosomia: High blood sugar levels can lead to excessive fetal growth, making childbirth more challenging.
- Preeclampsia: A serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and other symptoms. Women with diabetes are at a higher risk.
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM): If you develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, it’s crucial to follow your doctor’s recommendations for blood sugar control to minimize risks for you and your baby.
Prenatal Care and Delivery Planning
- Regular Prenatal Visits: Regular prenatal checkups and screenings are essential for monitoring your health and the baby’s development.
- Delivery Planning: Discuss your delivery plan with your doctor. Depending on various factors, your doctor might recommend a specific delivery time or method to ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
Postpartum Care and Long-Term Health
After childbirth, your focus shifts to postpartum care and long-term health:
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Continue to monitor your blood sugar levels for some time after childbirth, as your body adjusts and medication needs might change.
- Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding is beneficial for both mothers and babies. It’s generally safe for women with diabetes, although blood sugar levels might need further monitoring.
- Long-Term Diabetes Management: Whether you had pre-existing diabetes or gestational diabetes, continue to manage your diabetes effectively to reduce the risk of complications in the future.
Emotional Wellbeing and Support
Pregnancy can be an emotionally demanding time. Here’s how to prioritize your mental health:
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to manage stress and anxiety.
- Social Support: Build a strong support system of family, friends, or support groups for women with diabetes. Sharing experiences and concerns can be invaluable.
Technological Advancements in Pregnancy with Diabetes
Technology offers valuable tools for managing diabetes during pregnancy:
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): These devices provide real-time blood sugar data, allowing for proactive adjustments in diet or insulin to maintain optimal control.
- Diabetes Management Apps: Several apps help track blood sugar levels, food intake, medication doses, and fetal development.
- Telehealth Consultations: Remote consultations with your healthcare team can be convenient and offer additional support.
Looking Ahead: Research and Future Possibilities
Research in diabetes and pregnancy holds promise for future advancements:
- Improved Glucose Monitoring Technologies: Developments in continuous and non-invasive glucose monitoring methods are ongoing, aiming for greater comfort and convenience.
- Artificial Pancreas Systems for Pregnancy: Research is exploring the use of closed-loop insulin delivery systems during pregnancy to further automate and optimize blood sugar control.
- Personalized Medicine Approaches: Tailored treatment plans based on individual factors may become more prevalent, offering a more precise approach to diabetes management during pregnancy.
Conclusion
The journey of pregnancy with diabetes can be empowering. By planning ahead, collaborating with your healthcare team, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and utilizing available resources, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy for yourself and your baby. Remember, knowledge is power. With the information and support provided here, you can approach pregnancy with confidence and optimism.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge and should not be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor to create a personalized diabetes management plan before and during pregnancy.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago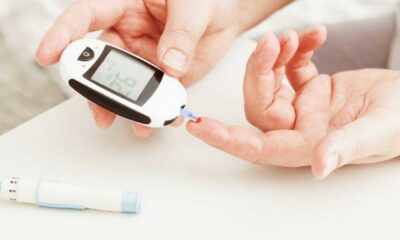
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago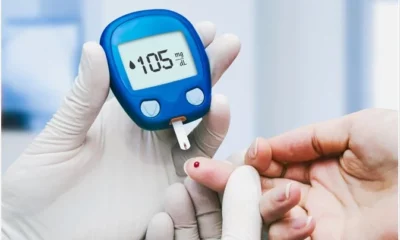
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago








