Diabetology
Demystifying Diabetes for a Clearer Understanding
Published
1 year agoon
By
Robert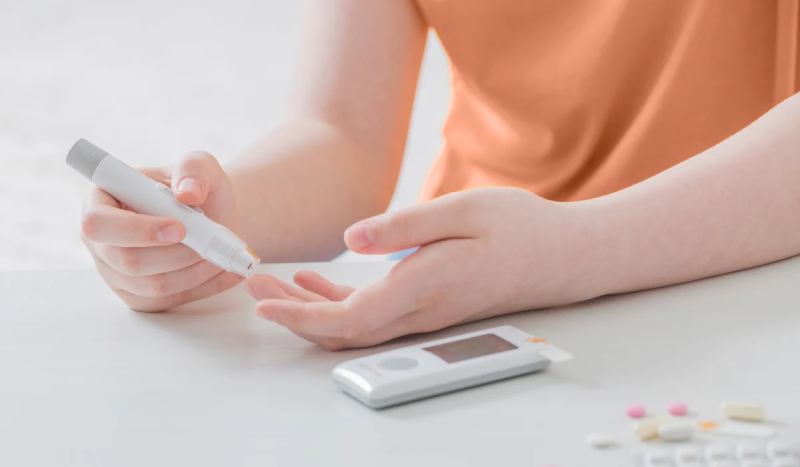
The word “diabetes” can evoke confusion and even fear. Images of needles, strict diets, and a lifetime of limitations might come to mind. But the reality of diabetes is much more nuanced. This guide aims to demystify diabetes, offering a clear understanding of the condition, its types, management strategies, and how to live a fulfilling life despite the diagnosis.
Unveiling the Basics of Diabetes
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus, often shortened to diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by chronically high blood sugar (glucose) levels. Glucose is the primary source of energy for our cells, and it gets into the cells with the help of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. In diabetes, this system malfunctions, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Types of Diabetes:
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D): This autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body produces little to no insulin. T1D typically develops in childhood or young adulthood and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes (T2D): This is the most common type of diabetes, affecting millions of people worldwide. In T2D, the body either develops insulin resistance (cells become less responsive to insulin) or doesn’t produce enough insulin to meet its needs. T2D often develops gradually and can sometimes be managed with lifestyle modifications, but medications may also be necessary.
- Gestational Diabetes (GD): This temporary form of diabetes develops during pregnancy in some women. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can affect insulin sensitivity, leading to high blood sugar levels. GD usually resolves after childbirth, but women with GD have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Unveiling the Warning Signs
Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Here are some common warning signs to be aware of, although it’s important to note that not everyone experiences all these symptoms, and some may have mild symptoms that go unnoticed:
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination: The body attempts to eliminate excess sugar from the blood through urination, leading to increased thirst and urination.
- Unexplained weight loss: When the body can’t use glucose for energy due to insulin deficiency, it may break down muscle and fat for fuel, leading to unintended weight loss.
- Increased hunger: The body may not be able to absorb glucose effectively due to insulin resistance, leading to increased hunger despite eating.
- Fatigue and lack of energy: Chronically high blood sugar levels can deprive cells of energy, leading to fatigue and tiredness.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive part of the eye, affecting vision and potentially leading to blindness.
- Slow-healing wounds: Diabetes can impair blood circulation and reduce the body’s ability to fight infections, leading to slow-healing wounds.
- Frequent infections: High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Skin problems: Diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage) can cause dry, itchy skin, or fungal infections.
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet: Neuropathy can also cause tingling, numbness, or pain in the hands and feet.
If you experience any of these warning signs, it’s crucial to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and to discuss potential treatment options.
Unveiling the Impact of Diabetes
While diabetes has no cure, early detection and effective management are essential to prevent serious health complications. These complications can develop over time and affect various organs and systems in the body. Some significant concerns include:
- Heart disease and stroke: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease (PAD).
- Nerve damage (neuropathy): Chronically high blood sugar can damage nerves throughout the body, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness. This can affect various areas, including the feet, hands, and digestive system.
- Kidney disease (nephropathy): High blood sugar can damage the kidneys, leading to a decline in kidney function and potentially kidney failure.
- Eye problems (retinopathy): Diabetes is a leading cause of blindness. It can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems and even blindness.
- Foot problems: Nerve damage and poor circulation in the feet can increase the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and even amputation. Proper foot care is crucial for people with diabetes.
Demystifying Management Strategies
Living with diabetes doesn’t mean giving up on living a healthy and fulfilling life. By taking charge of your health and implementing effective management strategies, you can control your blood sugar levels and minimize the risk of complications. Here’s a breakdown of key areas to focus on:
- Diet and Nutrition:
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods: Choose fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. These foods provide essential nutrients, keep you feeling full for longer, and help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Limit sugary drinks and processed foods: Sugary drinks and processed foods are high in carbohydrates and can cause blood sugar spikes. Opt for water, unsweetened tea or coffee, and whole-food snacks.
- Practice portion control: Pay attention to serving sizes and be mindful of how much you eat to avoid overeating and blood sugar spikes.
- Learn about carbohydrate counting: This method helps you estimate the amount of carbohydrates in your meals, allowing you to plan your meals and insulin doses accordingly.
- Consult a registered dietitian: A registered dietitian can create a personalized meal plan that fits your specific needs and preferences, ensuring you receive proper nutrition while managing your diabetes.
- Exercise and Physical Activity:
- Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and overall blood sugar control.
- Find activities you enjoy: Choose activities you find fun and can stick with long-term, such as walking, swimming, biking, dancing, or yoga.
- Start slowly and gradually increase intensity: If you’re new to exercise, start gradually and increase the duration and intensity of your workouts as your fitness level improves.
- Consult with your doctor before starting a new exercise program: It’s essential to discuss any limitations or concerns with your doctor before starting a new exercise program, especially if you have any complications related to diabetes.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring:
- Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels: Frequent blood sugar monitoring allows you to track your response to food, exercise, and medications, enabling adjustments to your diabetes management plan as needed.
- Work with your doctor to determine your target blood sugar range: Your target blood sugar range will vary depending on your individual factors.
- Use a blood sugar monitor and test strips: These tools allow you to measure your blood sugar levels at home.
- Learn how to interpret your blood sugar readings: Understanding your readings helps you identify patterns and make informed decisions about your diet, medications, and activity level.
- Medications:
- Follow your doctor’s medication plan carefully: Depending on your type of diabetes and its severity, your doctor may prescribe medications like oral medications or insulin. It’s crucial to take your medications exactly as prescribed for optimal blood sugar control.
- Understand how your medications work: Ask your doctor about how your medications work and their potential side effects.
- Never adjust your medications without consulting your doctor: If you experience any side effects or have concerns about your medications, always consult your doctor before making any adjustments.
Unveiling the Importance of Self-Care and Support
Taking Charge of Your Well-Being:
Living with a chronic condition like diabetes can take an emotional toll. Here are some tips to manage your emotional well-being and support yourself:
- Join a support group: Connecting with others living with diabetes can provide valuable information, encouragement, and a sense of community.
- Practice stress management techniques: Stress can worsen blood sugar control. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress effectively.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can disrupt hormones and blood sugar levels.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help: Diabetes management can be complex. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor, diabetes educator, or other healthcare professionals for help and support whenever needed.
Prioritizing Preventive Care:
- Schedule regular appointments with your doctor: Regular checkups allow your doctor to monitor your progress, adjust your treatment plan as needed, and screen for potential complications.
- Get recommended screenings: Early detection of complications is crucial for preventing serious health problems. Follow your doctor’s recommendations for screenings related to eye health, foot health, and kidney function.
- Take care of your oral health: Diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease and tooth infections. Practice good oral hygiene and schedule regular dental checkups.
Living a Fulfilling Life with Diabetes
Diabetes may be a chronic condition, but it doesn’t have to define you. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, taking charge of your treatment plan, and prioritizing your overall well-being, you can effectively manage your diabetes and live a long, healthy, and active life. Here are some additional tips for living a fulfilling life with diabetes:
- Set realistic goals: Don’t overwhelm yourself by trying to change everything at once. Set small, achievable goals related to diet, exercise, and blood sugar control. Celebrate your successes along the way, and gradually build on your progress.
- Find a support system: Surround yourself with positive and supportive people who understand your challenges and encourage you on your journey. This could include family, friends, a diabetes support group, or a therapist.
- Focus on the positive: Living with diabetes can be challenging, but it’s important to maintain a positive outlook. Focus on the improvements you’re making to your health and the benefits of a healthy lifestyle.
- Don’t give up: There will be setbacks and challenges along the way. Don’t let them discourage you. Learn from your experiences, adjust your approach if needed, and keep moving forward.
- Embrace a healthy lifestyle: View diabetes management as an opportunity to embrace a healthier lifestyle overall. Focus on making healthy choices that benefit your entire body and mind.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about the latest advancements in diabetes research and management. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about resources and educational materials available to you.
- Advocate for yourself: Be an active participant in your healthcare. Ask questions, express your concerns, and work collaboratively with your healthcare team to create a treatment plan that works best for you.
Remember: Knowledge is power. With the information and resources provided in this guide, you are well on your way to taking charge of your diabetes and living a fulfilling life. Don’t hesitate to ask questions, seek support, and work collaboratively with your healthcare team to create a personalized diabetes management plan that works best for you.
Conclusion
Demystifying diabetes can reduce fear and empower you to take control of your health. By understanding the different types, management strategies, and importance of self-care, you can effectively navigate your journey with diabetes. Embrace a healthy lifestyle, prioritize regular checkups and preventive care, and surround yourself with a supportive network. Remember, you are not alone in this. With a positive attitude, dedication, and the right support system, you can live a long and fulfilling life despite having diabetes.
Note:
This guide provides a general overview of diabetes. It’s crucial to consult with your doctor for personalized advice and treatment plans specific to your needs. The information provided is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice.
You may like
-


How to Monitor Blood Sugar at Home: A Beginner’s Guide
-


Diabetes Prevention 101: What You Need to Know
-


Diabetes Screening: Why Early Detection Saves Lives
-


How Blood Sugar Monitoring Can Help with Prediabetes
-


Essential Tips for Diabetes Prevention: How to Lower Your Risk Naturally
-


Understanding Glycemic Index Foods and Their Impact on Your Health
The Latest News
- Ayurvedic Remedies to Manage Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
- Scientists Discover Sweet and Simple Way to Reduce Diabetes Risk — No Medicine Required
- How AI Is Revolutionizing Diabetes Care: From Glucose Monitoring to Prevention
- Advancing Medical Innovations: Exploring the Breakthroughs of Microsurgery
- Your Natural Solution for Blood Sugar Control
- Natural Remedies to Control Diabetes at Home
- Diabetes and Heart Disease: Understanding the Dangerous Connection

Ayurvedic Remedies to Manage Type 2 Diabetes Effectively

Scientists Discover Sweet and Simple Way to Reduce Diabetes Risk — No Medicine Required

How AI Is Revolutionizing Diabetes Care: From Glucose Monitoring to Prevention

Lung growth invading Treg have different transcriptional profiles and capability connected to designated spot bar reaction

Psoriasis be treatment by adjuvant Salicylic acid, ceramides as this containing lotions

The CDC cautions physicians to be vigilant about uncommon, fatal flesh-eating germs
Trending
-
General Medicine4 days ago
Advancing Medical Innovations: Exploring the Breakthroughs of Microsurgery
-
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week agoYour Natural Solution for Blood Sugar Control
-
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days agoHow AI Is Revolutionizing Diabetes Care: From Glucose Monitoring to Prevention
-

 Diabetology6 hours ago
Diabetology6 hours agoAyurvedic Remedies to Manage Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
-

 Diabetology7 hours ago
Diabetology7 hours agoScientists Discover Sweet and Simple Way to Reduce Diabetes Risk — No Medicine Required
