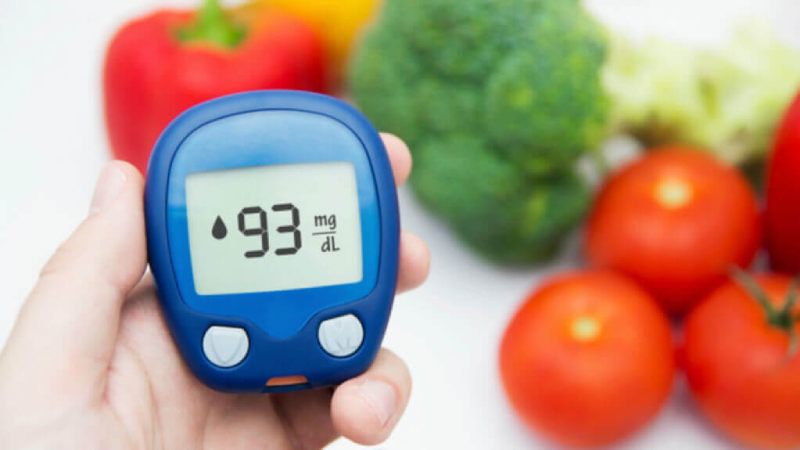
Understanding the subtleties of the glycemic index (GI) is essential for creating good eating habits. One important indicator of how quickly carbs in food raise blood sugar is the GI. High GI foods can cause blood sugar surges, which can be problematic for people controlling diabetes or trying to lose weight. Luckily, there are useful strategies to reduce the GI of your meals, mainly through the inclusion of foods that help to stabilize blood sugar levels. Here are some advice from experts to help you avoid sugar-spiking foods and choose healthier ones.
Go For Whole Grains:
Whenever feasible, choose whole grains over refined grains. Whole grains have a lower glycemic index because they are higher in minerals and fibre, which helps to delay the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Examples of whole grains are brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat.
Include legumes:
Legumes are a great source of fiber and protein. This includes beans, lentils, and chickpeas. Legumes provide you long-lasting energy and encourage feelings of fullness, so they can help reduce the total glycemic index of your diet.
Add In Some Good Fats:
Good fats, such those in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, can lessen the glycemic impact of a meal. By slowing down digestion, fats help to avoid sharp rises in blood sugar. For a healthy diet, include these fats in moderation in your meals.
Include Foods High In Protein:
Foods high in protein, like fish, lean meats, tofu, and Greek yogurt, can help control blood sugar levels by reducing the rate at which carbs are absorbed. Every meal should include some form of protein to help with overall glycemic control.
Give Attention To Non-starchy Veggies:
Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, and peppers are examples of non-starchy vegetables that are high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals yet low in calories and carbs. These veggies can be consumed in large quantities and have little effect on blood sugar levels.
Restrict Additional Sugar Intake:
Watch out for foods and drinks (soft drinks, candies, pastries, and processed snacks) that have added sugars. These foods can cause sharp rises in blood sugar levels since they usually have a high glycemic index. To sate your sweet desire without getting an unwelcome sugar surge, use naturally sweet options like fresh fruit.
Use Portion Control Techniques:
Be mindful of serving quantities to prevent overindulging, which may lead to blood sugar rises. Use smaller utensils, bowls, and plates to help manage portion sizes and avoid consuming too many calories.
Select Sugars With Low Glycemic Index:
When adding sweetness to food and drink, choose low-glycemic options such erythritol, stevia, or monk fruit. These substitutes offer sweetness without producing noticeable blood sugar spikes, which makes them good options for people trying to control their glycemic index.
Consume Meals That Are Balanced:
Aim for well-balanced meals that contain a mix of fiber, healthy fats, protein, and carbs. This combination contributes to a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels by slowing down the breakdown and absorption of carbs.
Remain Hydrated:
In addition to being beneficial for overall health, drinking enough water throughout the day can help control blood sugar levels. To maintain proper metabolic function and to stay hydrated, try to have at least 8 glasses of water each day.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago